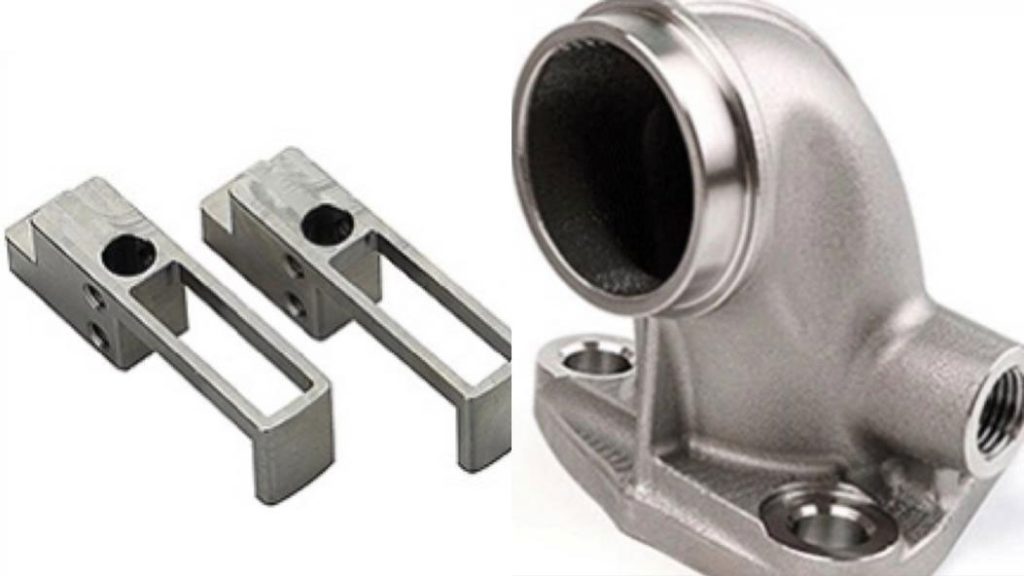
Injection molding and 3D printing are two popular manufacturing processes used to produce a wide range of products. Injection molding is a process where melted plastic is injected into a mold cavity, cooled, and then ejected as a finished product. 3D printing, on the other hand, is a process where a 3D model is created using a computer program and then printed layer-by-layer using materials such as plastic, metal, or resin. While both processes have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, understanding the differences between injection molding and 3D printing is important in determining which process is better suited for a particular application.
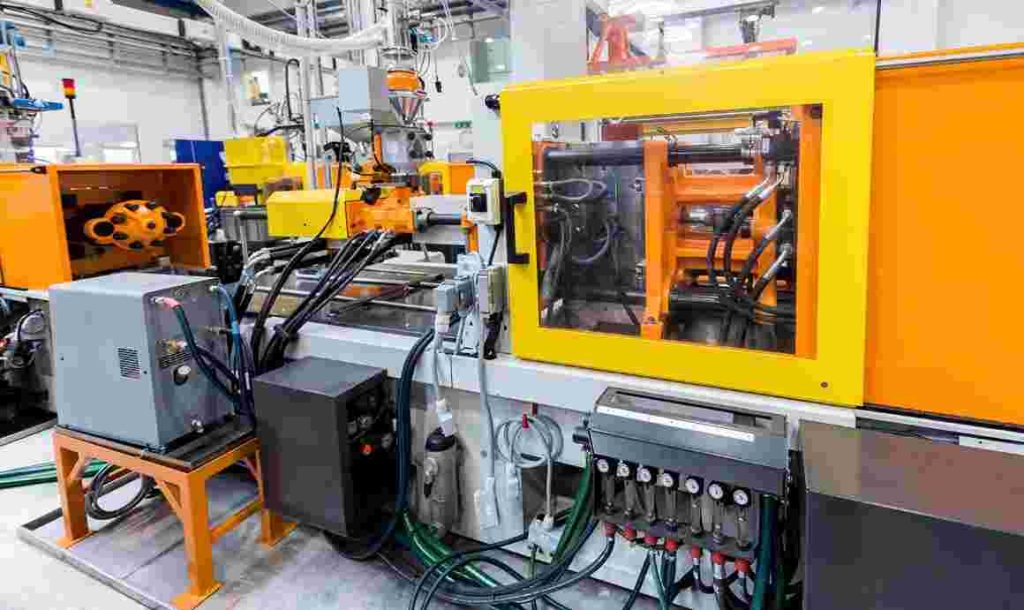

Advantages and disadvantages of injection molding
Advantages of injection molding include:
- High production efficiency: Injection molding can produce large quantities of parts quickly and consistently, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
- Design flexibility: Injection molding allows for a wide range of shapes, sizes, and complexities to be produced, with the ability to include features like inserts, threads, and undercuts.
- High precision and accuracy: Injection molding can produce parts with very tight tolerances and high precision, resulting in high-quality finished products.
- Cost-effective for large volumes: Due to the high initial setup cost, injection molding is typically more cost-effective for larger production runs.
Disadvantages of injection molding include:
- High initial tooling and equipment cost: Injection molding requires expensive tooling and equipment, making it more expensive for small production runs.
- Limited material options: While injection molding can use a wide range of materials, some materials may not be suitable for the process.
- Long lead time: The process of designing, producing, and testing molds can take time, resulting in longer lead times compared to other manufacturing methods.
- High material waste: Injection molding can generate a significant amount of scrap material during the production process, which can add to overall costs.
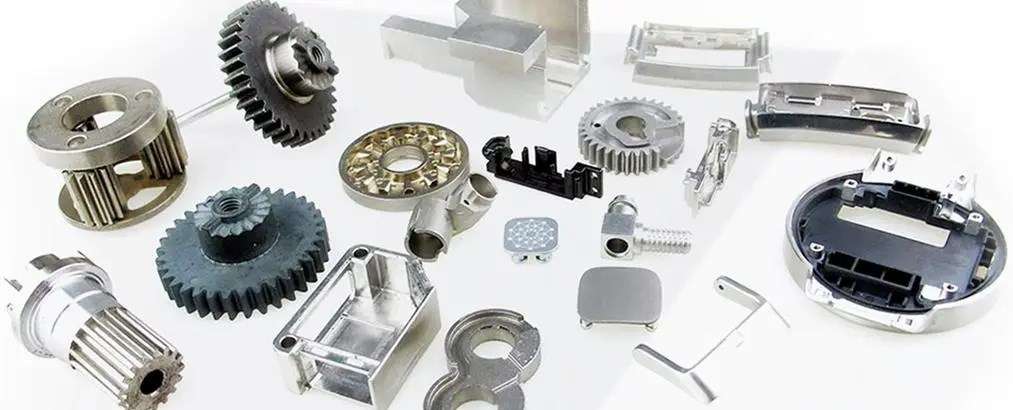

Advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has several advantages and disadvantages compared to other manufacturing processes.
The key advantages of 3D printing include:
- Design flexibility: 3D printing allows for the creation of complex and intricate designs that may not be possible with traditional manufacturing processes.
- Customization: 3D printing allows for the creation of one-of-a-kind parts, making it ideal for personalized products or prototypes.
- Reduced lead time: 3D printing can produce parts much faster than traditional manufacturing processes, reducing lead time and time to market.
- Material efficiency: 3D printing can use only the amount of material required for the part, reducing waste and material costs.
- Reduced tooling costs: 3D printing does not require expensive tooling or molds, making it cost-effective for small production runs.
The disadvantages of 3D printing, including:
- Limited materials: While 3D printing can use a variety of materials, the range is still limited compared to traditional manufacturing processes.
- Surface finish: Parts produced by 3D printing often require post-processing and finishing work to achieve a smooth surface finish.
- Limited part size: The size of parts that can be produced by 3D printing is limited by the size of the printer.
- Cost: While 3D printing can be cost-effective for small production runs, it can be more expensive than traditional manufacturing processes for large production runs.
- Limited strength: Parts produced by 3D printing may not have the same strength or durability as those produced by traditional manufacturing processes.
Overall, 3D printing and Injection Molding have their advantages and disadvantages. The choice between 3D printing and other manufacturing processes depends on the specific requirements of the application.

Differences between Injection Molding and 3D Printing
As Injection molding and 3D printing have their advantages and disadvantages, to properly use these two processes, you need to know other key differences including:
- Materials
Injection molding uses a variety of materials, including thermoplastics, metals, and ceramics, while 3D printing is typically limited to plastic, metal, and ceramic materials. However, newer 3D printing technologies are expanding the range of materials that can be used.
- Production volume
Injection molding is ideal for high-volume production runs, while 3D printing is better suited for producing smaller quantities or one-off parts.
- Accuracy and precision
Injection molding typically produces parts with higher accuracy and precision than 3D printing, especially when producing large quantities of parts.
- Cost
Injection molding has higher upfront costs for tooling and equipment, making it more expensive for smaller production runs, while 3D printing has lower setup costs and is more cost-effective for producing smaller quantities.
- Design flexibility
3D printing allows for greater design flexibility, including the ability to produce complex geometries and customized parts, while injection molding is better suited for producing parts with consistent and repeatable designs.
- Surface finish
Injection molding produces parts with smoother surface finishes than 3D printing, which can result in the need for post-processing and finishing work.
In summary, injection molding and 3D printing are two different manufacturing processes, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the application, including production volume, material selection, accuracy, and design flexibility.