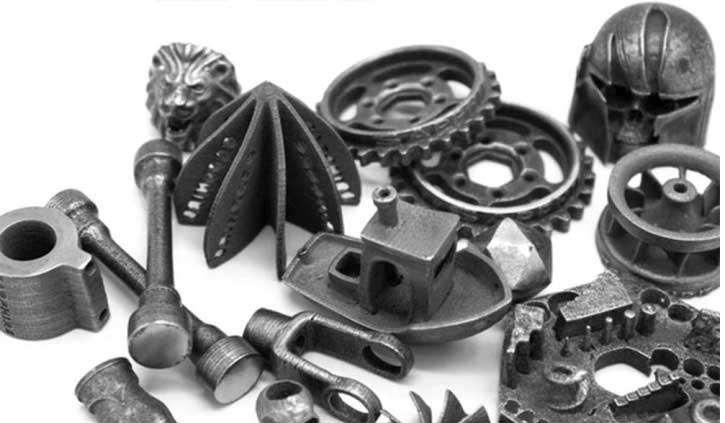
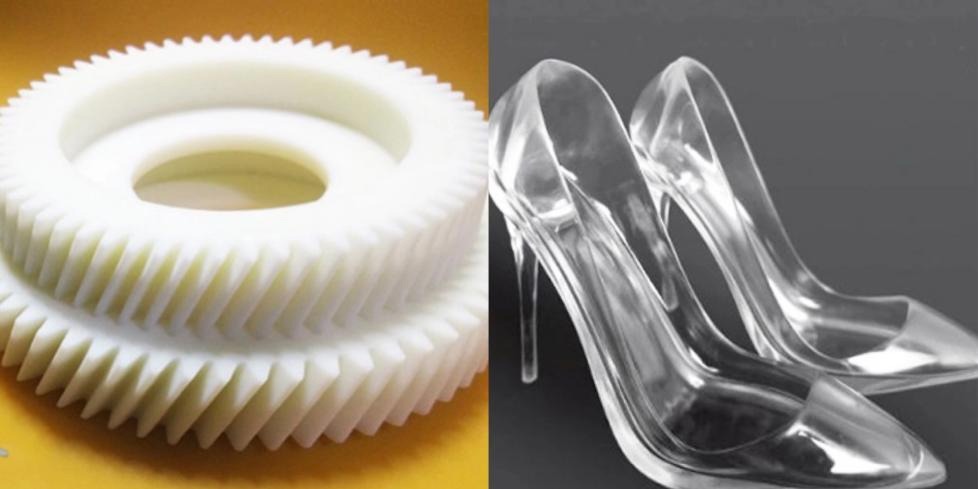
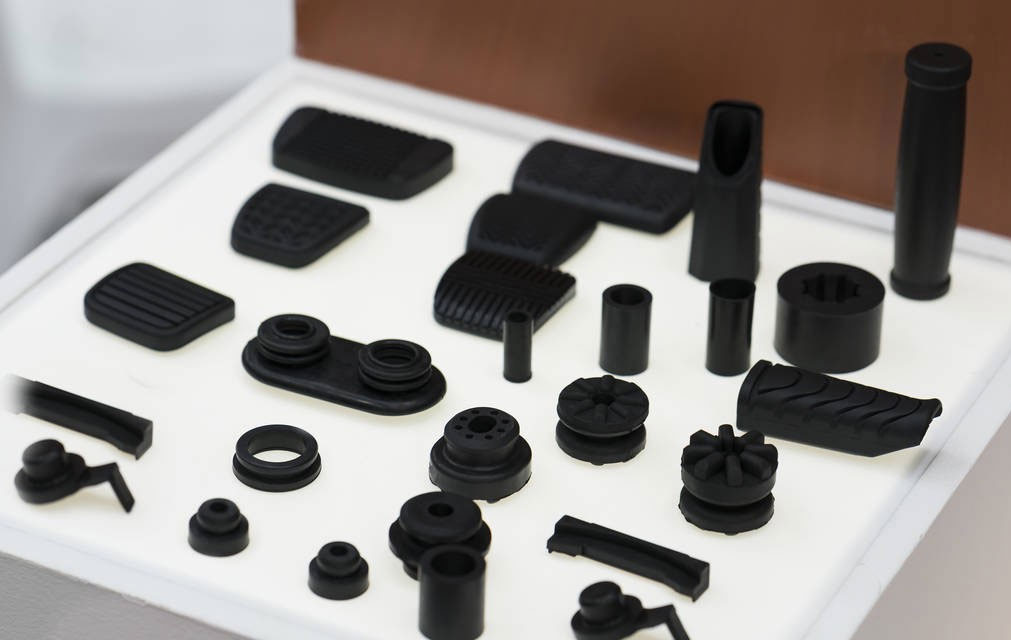
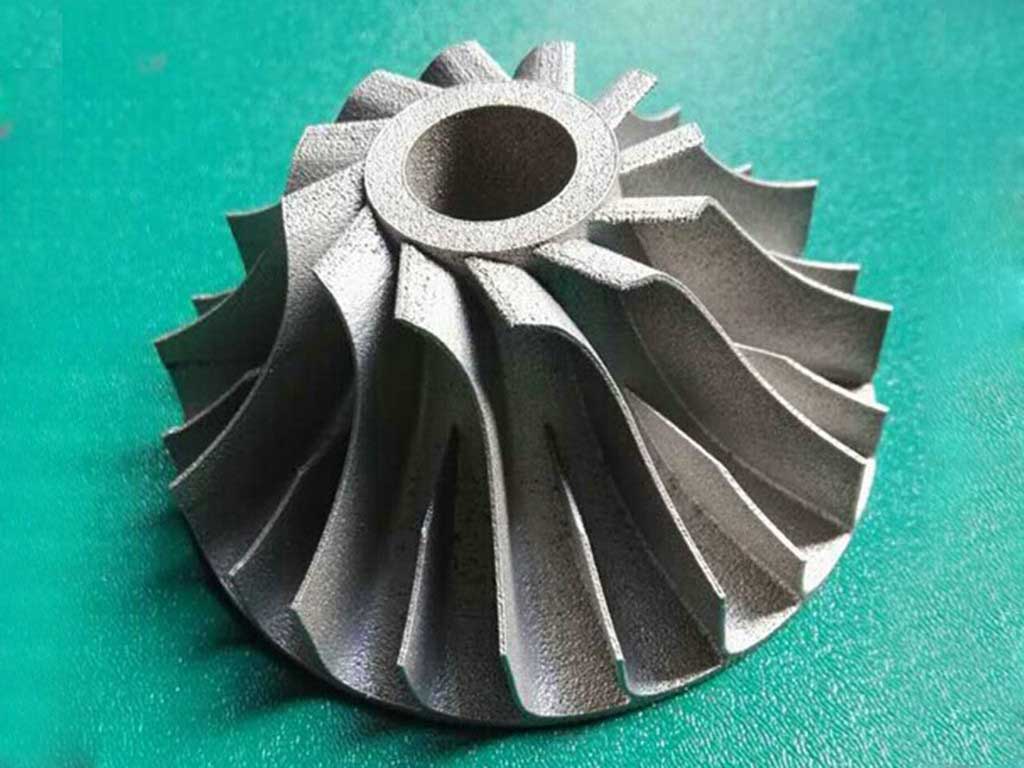
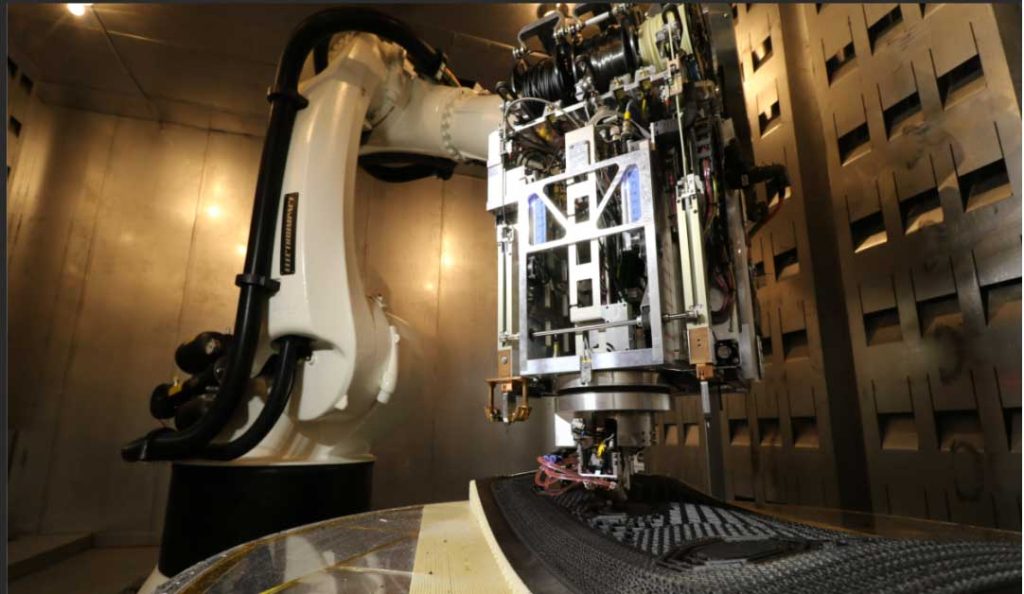
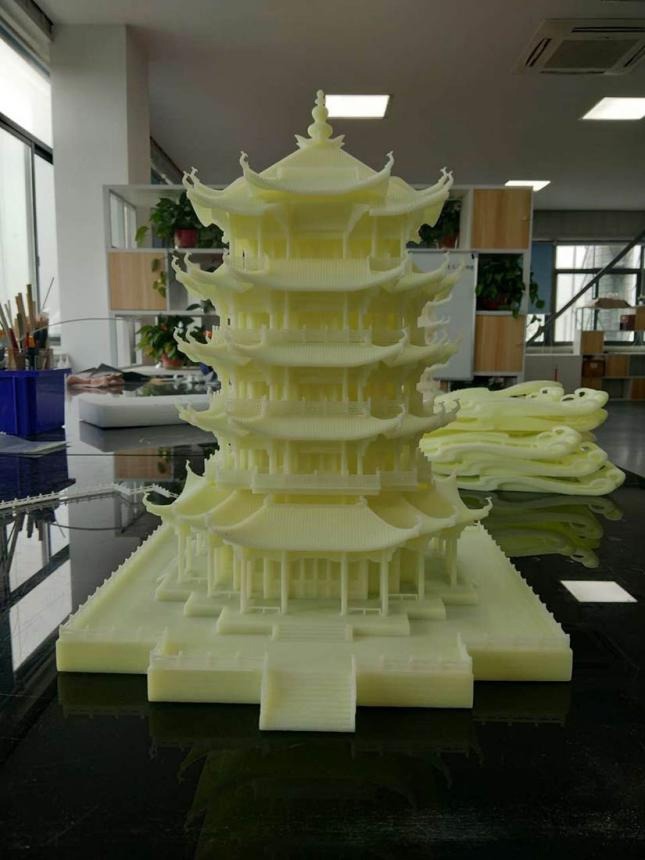
The application of 3D printing technology is the development trend of the future machinery manufacturing industry, and now the manufacturing industry has developed in the direction of digitalization. The application of 3D printing technology in the field of machinery manufacturing plays an important role in promoting the better development of the machinery manufacturing industry.
Why use 3D printing technology instead of CNC machining or mold machining?
Mechanical design drawing, from the initial hand, drawing to drawing on the computer. The introduction of software such as CAD has greatly improved the level of designers, and further improved the quality of drawings and the accuracy of processing. However, software such as CAD is only a plane drawing, and the cooperation between the parts can only rely on the overlapping of the drawings. The cooperation between more complex but small parts is difficult to be detailed so there is a big problem in the cooperation between parts.
The introduction of 3D drawing software is favored by the majority of designers for its three-dimensional sense of fit and intuitive design. Therefore, software such as Pro/Engineer is generally used by mechanical designers. However, the processed drawings are still the processing of plane drawings, and the designed parts need further processing. Sometimes parts are too small, making machining complex.
The machining of small parts with complex structures is very time-consuming. Even if it is processed by CNC machine tools, the programming of the processing is also very time-consuming. Moreover, only one or two experimental pieces can be processed, and the average cost is very high.
If you make a mold, you need to go through a lot of experiments, and the design of the mold may not be completed at one time. The cost of making a mold is very high.
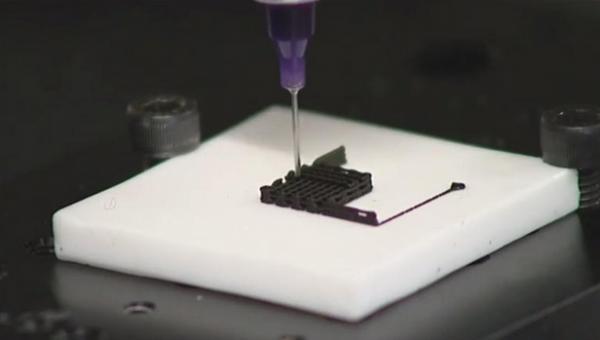
3D printing technology is based on digital model files, using adhesive materials such as powder metal or plastic, and stacking them through a nozzle or a laser beam. Including FDM technology, SLS technology, MJF technology, SLA, and other technologies.

With the improvement of 3D printing technology, the current FDM technology has been greatly improved, and the addition of laser technology has further improved processing accuracy. At present, most industrial-grade 3D printers basically adopt processing methods such as SLA.
After the mechanical parts are modeled by 3D software, the modeled parts are archived in STL format. After the 3D printer is connected to the computer, it will print the identified model, and the printed parts are consistent with the required size. Through these parts, it can be seen whether the structure of the parts and the related dimensions are more suitable for the product made. Moreover, there are not many materials for 3D printing, and the cost is greatly reduced.
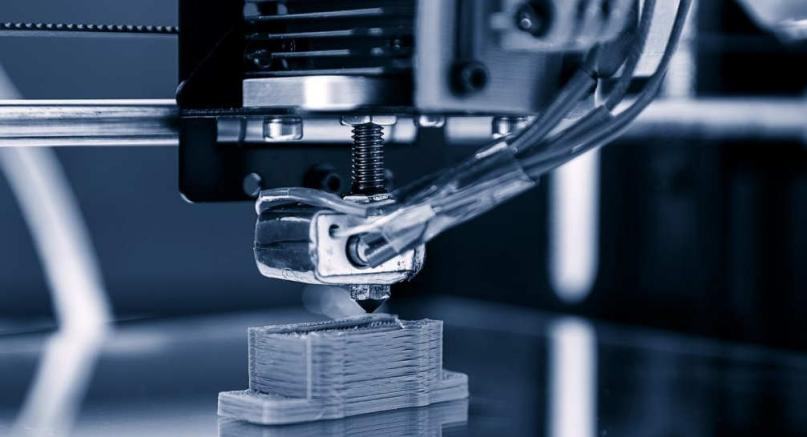

Applications of 3D printing in mechanical manufacturing
3D printing has numerous applications in mechanical manufacturing and offers several advantages in specific areas. Here are some key applications and advantages:
- Prototyping: 3D printing allows rapid prototyping of mechanical parts, enabling designers and engineers to quickly iterate through designs and concepts. This significantly reduces the time and cost associated with traditional prototyping methods like CNC machining or injection molding.
- Customization: One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing is its ability to produce highly customized parts and products. This is particularly useful in mechanical manufacturing, where bespoke components may be required for specific applications or for fitting into unique assemblies.
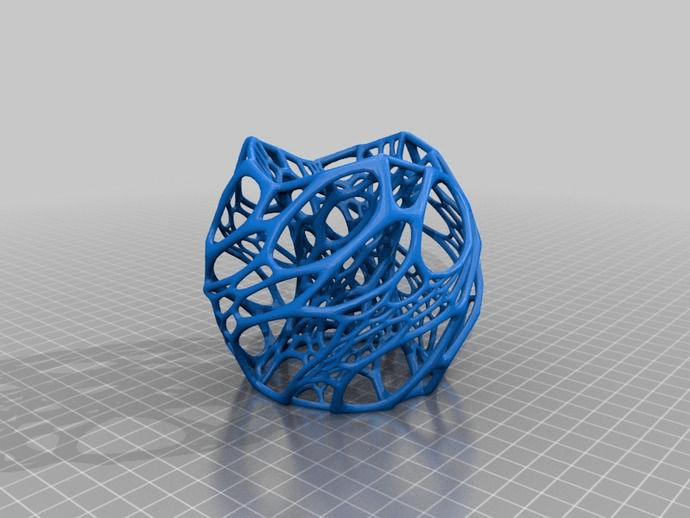
- Complex Geometry: Traditional manufacturing methods often struggle with complex geometries, whereas 3D printing excels in this area. It can produce intricate designs and structures that would be challenging or impossible to manufacture using conventional methods.
- Tooling and Fixtures: 3D printing is increasingly used for producing tooling, jigs, and fixtures in mechanical manufacturing processes. These aids can be tailored precisely to the requirements of a particular manufacturing process, improving efficiency and quality.
- Low-Volume Production: For low-volume production runs, 3D printing can be more cost-effective than traditional manufacturing methods like injection molding or die casting. It eliminates the need for expensive molds or tooling, making it ideal for producing small batches of parts economically.
- Reduced Material Waste: Unlike subtractive manufacturing methods such as milling or turning, which generate significant material waste, 3D printing is an additive process that only uses the material necessary to build the part. This leads to reduced material waste and lower overall material costs.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: 3D printing enables on-demand manufacturing, where parts can be produced as and when needed, reducing the need for large inventories and minimizing lead times. This flexibility can be particularly advantageous in industries where demand for parts is variable or unpredictable.
- Assembly Consolidation: With 3D printing, it’s possible to consolidate multiple components into a single printed part, reducing the need for assembly and potentially improving the overall strength and integrity of the final product.
- Material Variety: 3D printing supports a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites. This versatility allows manufacturers to choose the most suitable material for their specific application, whether it be for strength, heat resistance, conductivity, or other properties.
- Design Optimization: The design freedom offered by 3D printing allows for the optimization of parts and assemblies, leading to improved performance, reduced weight, and enhanced functionality. This can result in more efficient mechanical systems and products.
In summary, 3D printing has numerous applications in mechanical manufacturing, offering advantages such as rapid prototyping, customization, complex geometry capabilities, reduced material waste, and more. Its versatility and ability to produce parts on-demand make it an increasingly valuable tool in modern manufacturing processes.
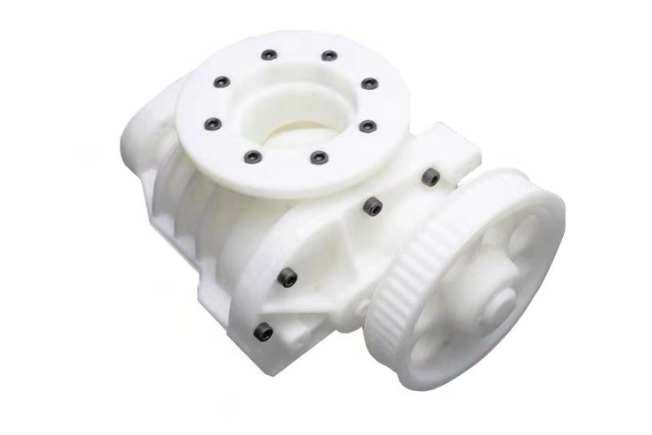

JTR is able to provide a variety of 3D printing technologies, including carbon DLS, DMLS, FDM, MJF, SLS, SLA, and other technology types. Professional technicians and production equipment are ready to serve you.