CNC turning is a critical and widely used manufacturing process that plays a pivotal role in the creation of cylindrical parts with high precision and consistency. This process is integral to many industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer goods. The core functionality of CNC turning revolves around the automation of machining operations via a Computer Numerical Control (CNC) system.

How CNC Turning Works
The process of CNC turning can be broken down into four key steps:
- Programming: CNC turning begins with programming, where operators define the machining operations required for the part. This includes specifying dimensions, cutting tool paths, speed, feed rate, and any additional operations such as facing or threading. The program is loaded into the CNC controller.
- Setup: The workpiece is mounted securely on the lathe’s spindle, and the cutting tool is installed in the tool holder. Calibration ensures accurate positioning of the tool in relation to the workpiece.
- Machining: During machining, the CNC lathe rotates the workpiece, and the cutting tool follows the programmed path, removing material in layers. Continuous monitoring ensures that the machining process stays within the required specifications.
- Inspection and Finishing: Once machining is complete, the part is inspected to ensure that it meets the desired dimensions and tolerances. If necessary, finishing operations like deburring or polishing are performed to refine the surface finish.
CNC Machining Processes

CNC Milling Service
CNC Milling uses 3-axis milling and 5-axis indexed milling to rapidly cut a choice of more than 30 engineering-grade thermoplastics and metals into complex shapes and precision components.
As one of the subtractive manufacturing processes, milling removes material from bulk by using tools to cut/drill a workpiece. CNC Milling is capable of producing parts with high accuracy at a high speed.

CNC Turning Service
CNC Turning uses a lathe to create detailed functional prototypes and end-use parts with cylindrical features. It removes material from bulk by rotating the workpiece.
CNC Turning is great for the processing of cylindrical parts, capable of producing high-quality parts cost-effectively.
Main Components of a CNC Lathe
The CNC lathe consists of several essential components that facilitate the turning process:
| Component | Function |
| Headstock | Holds the spindle, which rotates the workpiece. |
| Chuck | Grips the workpiece securely. |
| Turret | Holds multiple cutting tools for automatic tool changes. |
| Tool Post | Secures the cutting tool in manual lathes (CNC uses a turret). |
| Tailstock | Supports long workpieces with a center or live tooling. |
| Control Panel | Inputs CNC programs (G-code) and monitors operations. |
| Coolant System | Cools and lubricates the cutting area to prevent overheating. |
Common CNC Turning Operations
Some of the most common operations carried out on a CNC lathe include:
| Operation | Description |
| Facing | Flattens the end of the workpiece for a smooth surface. |
| OD Turning | Shapes the outer diameter (OD) of the part. |
| Boring | Enlarges or finishes internal diameters (ID). |
| Drilling | Creates holes in the center or along the axis. |
| Taper Turning | Produces conical shapes using angled tool paths. |
| Grooving | Cuts narrow channels (e.g., for O-rings). |
| Threading | Produces internal or external screw threads. |
| Knurling | Adds a textured grip pattern for handles. |
Advantages of CNC Turning
CNC turning offers a host of benefits, making it highly favored in precision manufacturing:
- High Precision: CNC turning allows for extremely precise control over dimensions, with tolerances often measured in micrometers, making it ideal for applications requiring high accuracy.
- Consistency: Since CNC turning is automated, each part produced is identical to the next, ensuring consistent quality and performance.
- Versatility: CNC turning can handle a wide range of cylindrical parts, from basic shafts to complex geometries. It can perform multiple operations in a single setup, reducing machine downtime and increasing overall efficiency.
- Efficiency: The automation involved in CNC turning reduces the need for manual intervention, leading to faster production and increased productivity.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in CNC equipment may be high, the long-term cost benefits, including reduced labor, improved productivity, and decreased scrap rates, make CNC turning a cost-effective solution.
Common Applications of CNC Turning
CNC turning is used extensively in various industries for parts requiring rotational symmetry. Some of its applications include:
- Automotive: Components like shafts, gears, and bushings.
- Aerospace: Parts such as turbine blades and engine components.
- Medical Devices: Precision implants, surgical tools, and prosthetics.
- Consumer Electronics: Parts like knobs, housings, and connectors.
- Industrial Machinery: Components like valves, pumps, and spindles.
Types of CNC Turning Machines
CNC turning machines vary in their design to suit different production needs:
- Horizontal CNC Lathes: These machines are best for larger workpieces and high-production environments.
- Vertical CNC Lathes: These are ideal for smaller components, providing better access to the workpiece and improved precision.
- CNC Swiss Lathes: Designed for small, intricate parts, these lathes are commonly used in industries like medical devices, where tight tolerances are essential.
The Role of CNC Turning in Modern Manufacturing
CNC turning has become an integral part of modern manufacturing, thanks to advancements in technology. It enables manufacturers to produce high-quality, complex parts with increased speed, efficiency, and minimal waste. Automation has made CNC turning a critical process in industries that require high-precision components.
Conclusion
In summary, CNC turning is an indispensable manufacturing process that offers precision, flexibility, and speed. From producing small, intricate parts to large, heavy-duty components, CNC turning is a versatile solution in modern manufacturing. By understanding how CNC turning works, manufacturers can make informed decisions about equipment and technology choices to optimize their production processes.
Our CNC Machining Center
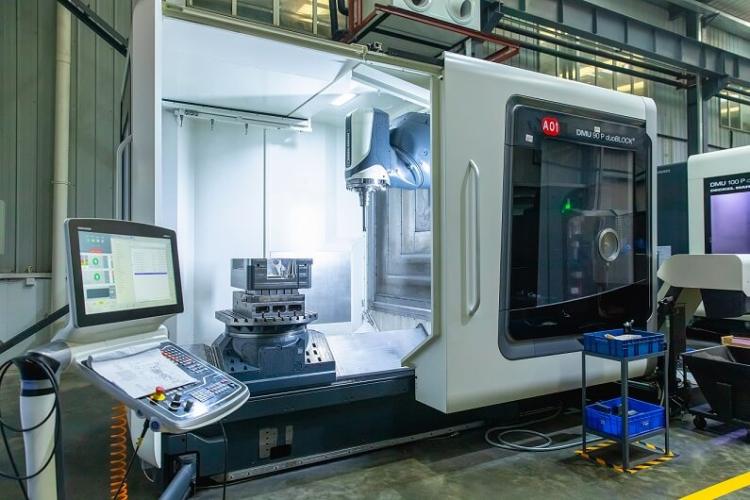
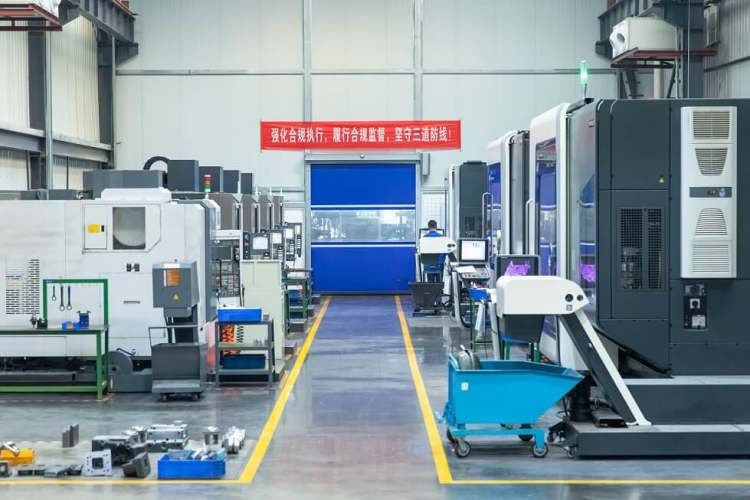


Our CNC machining center has more than 70 advanced equipment, which is equipped with 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machines, able to manufacture parts that meet most requirements from customers. In addition to CNC machining centers, there are also advanced full-automatic die casting machines from 300T to 1000T with an annual capacity of million pieces of parts.