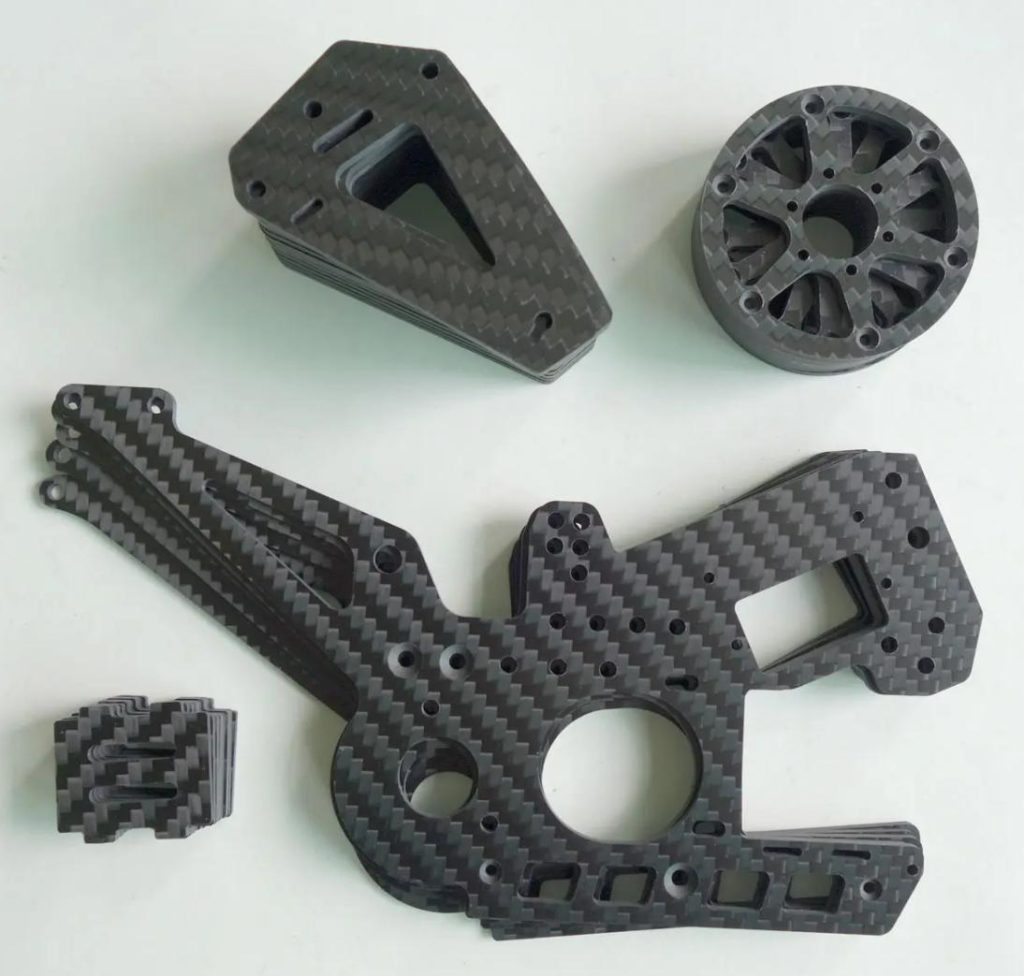
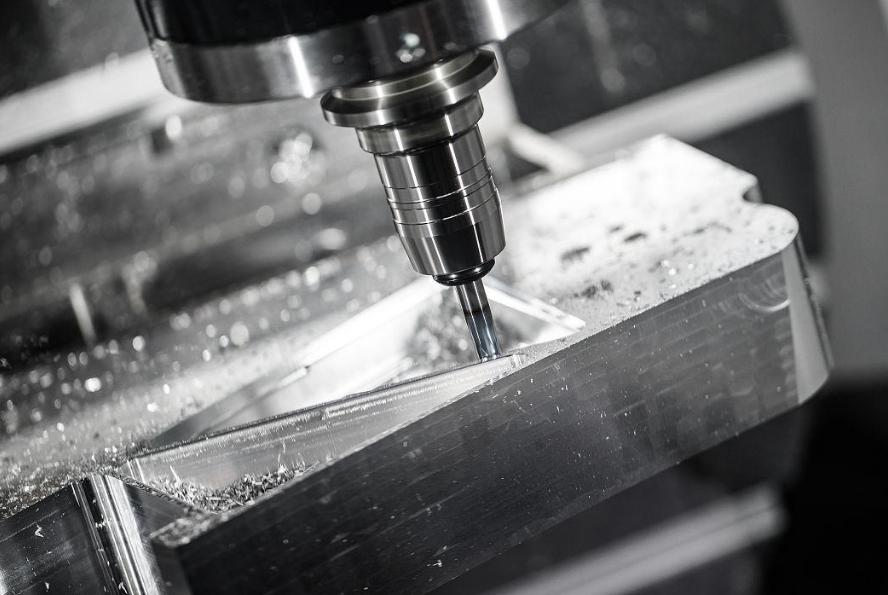
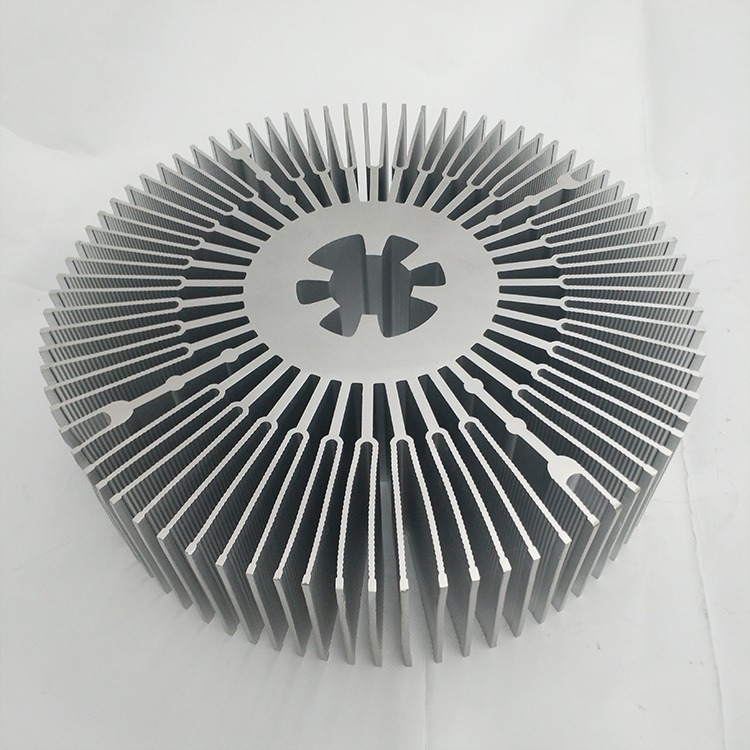
CNC milling is a vital process in modern manufacturing, delivering precision and efficiency across industries. However, the costs associated with CNC milling can vary significantly, influenced by numerous factors. Whether you’re developing a prototype or scaling up production, understanding these factors is crucial to managing expenses effectively. Here we delves into the top six factors that significantly influence the cost of CNC milling operations.
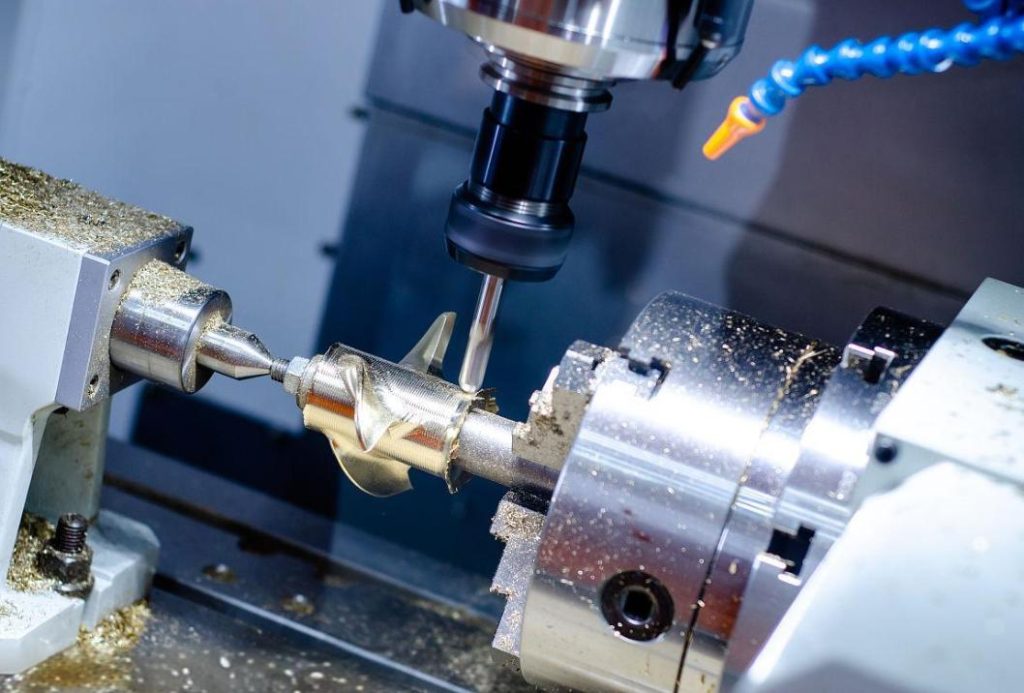

Factor 1: Material Type and Size
The choice of material and its dimensions play a foundational role in CNC milling costs. Different materials exhibit varying degrees of hardness, machinability, and cost.
Material Cost
The market prices of different materials vary significantly. For instance, common aluminum alloys are relatively inexpensive, while high-performance materials like titanium alloys and nickel-based alloys are costly. In CNC milling, if expensive materials are used, material costs will account for a larger proportion of the total milling cost. This is because these high-performance materials are not only expensive themselves, but they may also require special processing techniques and tools due to their unique physical and chemical properties, such as high hardness, high strength, and high corrosion resistance, further increasing processing costs.
Material Machinability
Material machinability also has a significant impact on milling costs. Easily machinable materials, such as soft aluminum alloys, can be milled at high cutting speeds and feed rates, resulting in short processing times and minimal tool wear. However, difficult-to-machine materials, such as stainless steel and titanium alloys, require lower cutting speeds and feed rates due to their higher hardness, toughness, or chemical reactivity, and they also experience rapid tool wear. This leads to longer processing times and frequent tool changes, thereby increasing milling costs.
Material Size and Weight
Larger workpieces require more material, leading to increased material costs. Additionally, handling and machining larger components often require specialized equipment and may increase labor costs.
The selection of the appropriate material is crucial for cost optimization. JTR CNC milling service can machining materials like aluminum, stainless steel, plastic, cooper, titanium, etc. Feel Free to contact us for your needs.

Factor 2: Design Complexity
The complexity of the part design directly influences the time and effort required for CNC machining. Specific performances are:
Part Complexity
Programming Complexity: Complex part designs require more sophisticated CNC programming. For instance, parts with intricate internal structures or irregular external shapes demand more time from programmers to plan tool paths, set cutting parameters, and so on. This not only increases the workload for programming but may also necessitate more advanced programming software and skilled personnel, thereby raising programming costs.
Increased Processing Time: Complex parts often require more processing steps and operations. For example, a part with multiple surfaces and fine features may need multiple setups, tool changes, and adjustments to cutting parameters, significantly increasing processing time and, consequently, milling costs.
Special Processing Requirements: Complex parts may necessitate special processing techniques or equipment. For example, parts with minute features might require micro-milling technology, which demands specialized micro-milling equipment and a high-precision processing environment, adding to the overall cost.
Tolerance Requirements
Increased Processing Difficulty: Tighter tolerance requirements imply higher processing precision. In CNC milling, achieving high-precision tolerances necessitates finer cutting parameters, more precise equipment and tooling, and more frequent inspection and adjustments during processing. This increases the difficulty and complexity of processing, thereby raising milling costs.
Impact on Scrap Rate: Strict tolerance requirements can lead to an increased scrap rate. If processed parts fail to meet the tolerance requirements, they become scrap, wasting raw materials, processing time, and tooling resources. To reduce the scrap rate, stricter quality control measures, such as increased inspection frequency and the use of more advanced inspection equipment, may be necessary, which in turn increases milling costs.
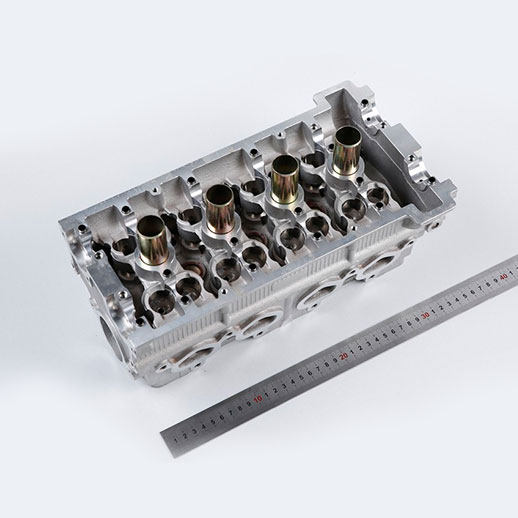

Factor 3: Production Volume
Production volume significantly impacts CNC milling costs, with economies of scale playing a critical role in determining unit prices.
Processing Time
Impact of Cutting Parameters: Cutting parameters (such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut) directly affect processing time. Appropriate cutting parameters can shorten processing time while ensuring processing quality. However, if cutting parameters are set improperly, such as too low a cutting speed or too small a feed rate, processing time will be excessively long. For example, when machining a large part, if the cutting speed is set too low, although it may improve processing accuracy, it will multiply the processing time, thereby increasing milling costs.
Sequence of Machining Processes: The sequence of machining processes can also affect processing time. An optimized machining sequence can reduce unnecessary setups, tool changes, and other operations, improving processing efficiency. Conversely, an unreasonable machining sequence may cause the part to be transferred frequently between the machine tool and fixture during processing, increasing auxiliary time and, consequently, milling costs.
Number of Parts
Economies of Scale: When the number of parts is large, economies of scale can be achieved. In large-scale production, batch production can be adopted, and by optimizing the processing process, arranging the production plan reasonably, and so on, the average cost of each part can be reduced. For example, in the production of automotive parts, due to the huge output, special fixtures, efficient production processes, and other methods can be used to reduce milling costs.
Composition of Unit Cost: For small-batch or single-piece production, each part needs to bear more fixed costs, such as programming costs and equipment debugging costs. Because these costs cannot be distributed to a large number of parts, the unit milling cost is relatively high.

JTR as a cnc milling and turning parts manufacturer, has more than 70 CNC equipments including 3-5 axis machining centers. We can provide all types of customized CNC milling parts to meet your project needs. Our experienced engineers will design the milling process and select the appropriate tool based on your drawings, then do the milling quickly while obtaining a good processing surface. By maintaining our strict tolerances, we ensure you the best quality. Contact us for your CNC machining needs.
Factor 4: Machine and Tooling Type
The type of CNC machine and tooling used for a project impacts both performance and costs.
Equipment Type
CNC milling machines come in various types, such as 3-axis and 5-axis milling machines. 3-axis milling machines are more commonly used for processing relatively simple parts and have a simpler structure and lower price. 5-axis milling machines, on the other hand, can process more complex parts, such as complex curved surfaces, but they have a higher equipment cost. This is because 5-axis milling machines are more technologically advanced, and their multi-axis linkage function requires more precise mechanical structures, control systems, and greater research and development investment.
When choosing the type of equipment, enterprises need to weigh their processing needs against their budget. If the main processing is simple planar or regularly shaped parts, 3-axis milling machines may be a more economical choice; however, if complex components in fields such as aerospace and automotive molds need to be processed, 5-axis milling machines, although with high equipment costs, can meet the processing requirements of complex shapes.
Equipment Cost
Purchase Cost: The purchase cost of equipment is a significant component of milling costs. High-end CNC milling machines, especially those with high precision, high speed, and multi-axis linkage functions, can cost hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars. These machines integrate advanced numerical control systems, high-precision transmission components, and high-performance spindles, and their research and development and production costs are high, making them expensive to purchase.
Operating Cost: Operating a CNC milling machine consumes electricity, and the power consumption of different power equipment varies. Although higher-power equipment may have higher processing efficiency, it also comes with higher electricity costs. In addition, the equipment needs to be regularly replaced with consumables such as coolant and lubricant during operation, which is also part of the operating cost.
Maintenance Cost: To ensure the precision and normal operation of the CNC milling machine, regular maintenance is required. This includes cleaning the equipment, inspecting and replacing key components, upgrading the numerical control system, etc. High-precision equipment has higher requirements for the maintenance environment and technicians, and its maintenance cost also increases accordingly. For example, some high-end imported CNC milling machines have high replacement costs for their components and require professional technicians for maintenance, which undoubtedly increases the maintenance cost of the equipment.

Tool Cost
Tool Material: The material of the tool directly affects its cost. Common tool materials include high-speed steel and cemented carbide. High-speed steel tools are relatively low-cost but have lower hardness and wear resistance; cemented carbide tools have higher hardness, wear resistance, and hot hardness, and can work at higher cutting speeds, but their cost is several times that of high-speed steel tools. For example, when processing materials with higher hardness, using cemented carbide tools, although costly, can improve processing efficiency and quality.
Tool Coating: To improve the cutting performance and service life of tools, many tools are coated. There are many types of tool coatings, such as titanium nitride coating and diamond coating. Coated tools can reduce cutting forces, increase cutting speed, and reduce tool wear, but the coating process is complex, which increases the cost of the tool.
Tool Geometry: Tools with different geometric shapes are suitable for different machining tasks. For example, ball-nose end mills are suitable for processing curved surfaces, while end mills are often used for processing planes and contours. Tools with special geometries, such as those with special blade shapes or multi-blade structures, have complex manufacturing processes and are relatively high in cost. When selecting tools, it is necessary to choose the appropriate tool geometry according to the specific processing requirements, while also considering cost factors.

Factor 5: Post-processing Methods
Post-processing is often necessary to achieve specific surface finishes or mechanical properties, but it can add significantly to overall costs. Such as:
Surface Treatment:
Processing Cost: Many parts require surface treatment after CNC milling, such as coating, anodizing, and electroplating. These surface treatment processes have their own costs. For example, electroless nickel plating is relatively expensive because it requires specific chemical solutions, equipment, and operating environments, and the process is relatively complex.
Impact of Quality Requirements: The quality requirements of surface treatment also affect costs. If the surface treatment is required to achieve a high degree of smoothness, uniformity, or specific performance indicators (such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, etc.), it may require more advanced surface treatment processes or an increase in the number of treatments, thereby increasing costs.
Customized Part Processing
Cost of Special Requirements: Customized parts often have special requirements in CNC milling, such as special hole positions, shapes, or dimensions. These special requirements may require additional processing steps or specialized tools. For example, when processing a part with a non-standard hole pattern, it may be necessary to redesign the fixture or use a special machining process, which will increase the processing cost.
Cost of Design Changes: If a customer requests a design change during the customized part processing, it will result in adjustments to the processing plan, scrapping of some processed parts, and reprogramming, thereby increasing milling costs.

Factor 6: Labor and Lead Time
Labor and lead time are key factors that affect CNC milling costs, especially when deadlines or specialized skills are involved.
Delivery Time
Rush Production Costs: If a customer requires a shorter delivery time, the company may need to arrange rush production. Rush production may require adjusting the production schedule, prioritizing the processing of this order, and may even require overtime work. This will increase labor costs, equipment usage costs, and other costs, resulting in additional rush production costs.
Production Schedule Adjustment Costs: In order to meet the delivery time requirements, the company may need to adjust the entire production schedule. This may affect the production progress of other orders, leading to delays in other orders or increased management costs. For example, in order to complete an urgent order in a short period of time, the company may need to suspend other ongoing orders and rearrange equipment, personnel, and raw materials, which will lead to a series of cost increases.
Labor Costs
Programming Personnel Costs: CNC milling programming work requires professional programmers. The technical level, experience, and salary level of programmers will affect programming costs. Experienced and skilled programmers can write more efficient and accurate numerical control programs, but their salary costs are also relatively high.
Operator Costs: Operators are responsible for operating CNC milling machines to process parts. The skill level, working hours, and wages of operators will affect operator costs. Skilled operators can better control equipment and reduce errors during the processing process, but their wages will also increase with their skill level.
Quality Control Personnel Costs: Quality control is crucial in CNC milling. Quality control personnel need to inspect the processed parts to ensure that they meet quality requirements. The inspection work of quality control personnel requires time and effort, and their salary costs are also part of the milling costs.

JTR uses the latest CNC machines to produce high-precision and fast-milling parts, the fastest time is within one day, to offer our customers a very short lead time. With a super cooperative professional work team, we can make the production cost at the lowest level by shortening the production time, labor cost.
For surface finishing needs, we also can providing you various options such as painting, anodizing, and chrome plating, etc. We at the same time can offer you some free services such as parts assembling which will be based on your needs. Believe JTR can providing you high quality products with reliable service.
In summary, the cost of CNC milling is affected by a combination of factors such as equipment, materials, design, production, post-processing, and others. In actual production, companies need to comprehensively consider these factors and reduce CNC milling costs and improve the company’s economic efficiency through measures such as optimizing equipment selection, reasonably selecting materials, improving design schemes, improving production efficiency, controlling post-processing costs, and rationally arranging labor.