CNC milling is a highly versatile manufacturing process, used across industries to create precise and complex parts. The choice of material—plastic or metal—can significantly impact the final product’s performance, cost, and durability. Each material offers unique advantages and is suitable for specific applications, making the decision critical to the success of the project. Here we will explore the characteristics of plastic and metal in CNC milling, helping you determine which material is better suited for your needs.
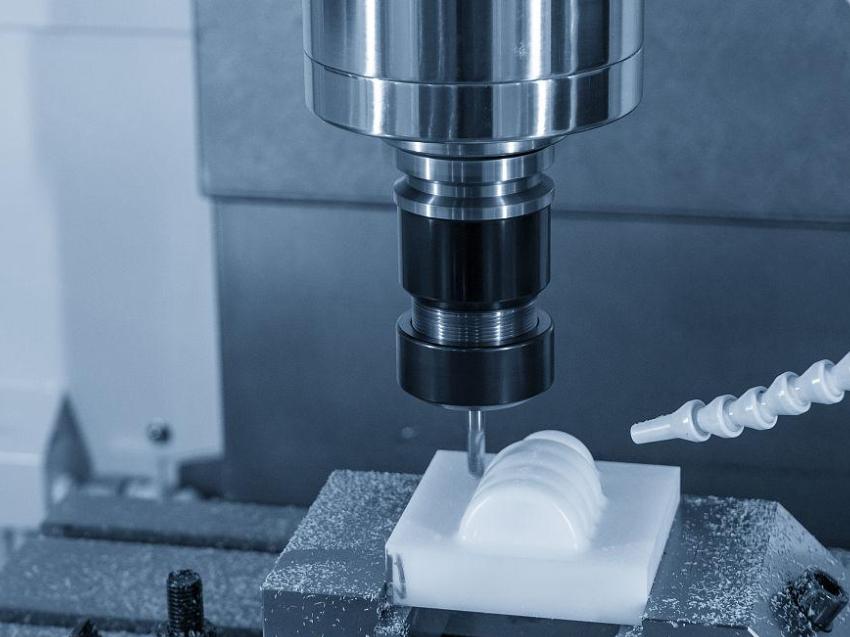

Plastic in CNC Milling
Plastics have become increasingly popular in CNC milling, thanks to their lightweight nature, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. CNC machining plastic parts are widely used for prototyping, low-strength applications, and non-conductive parts. Common plastic materials include ABS, polycarbonate, nylon, and polyoxymethylene, which are not only easy to process but also relatively low in cost.
Benefits of Using Plastic in CNC Milling:
- Cost-Effective: Plastics are generally less expensive than metals, both in raw material cost and machining expenses. Their softer nature allows for faster cutting, reducing production time and tool wear.
- Lightweight: Plastics are significantly lighter than metals, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Corrosion Resistance: Unlike metals, plastics are immune to corrosion, making them suitable for environments where exposure to moisture or chemicals is a concern.
- Electrical Insulation: Plastics provide excellent electrical insulation, making them a preferred choice for electronic components and housings.
Challenges of Using Plastic in CNC Milling:
- Lower Strength: Plastics generally offer lower tensile strength and durability compared to metals, limiting their use in high-stress applications.
- Thermal Sensitivity: Plastics can deform or melt under high temperatures, requiring careful management of cutting speeds and feeds.
Plastic is a versatile material in CNC milling, offering benefits in cost, weight, and corrosion resistance. However, its lower strength and thermal sensitivity make it more suitable for specific applications where these properties are less critical.
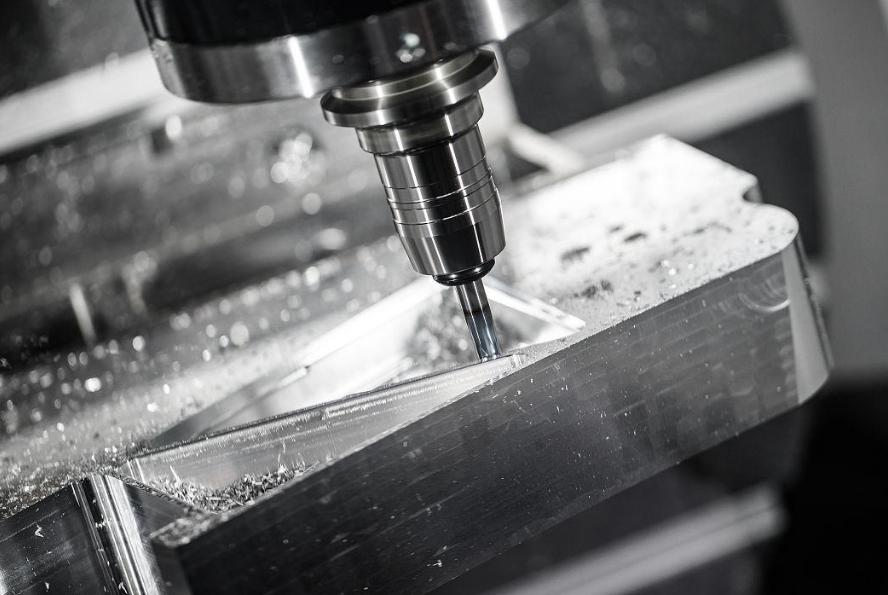

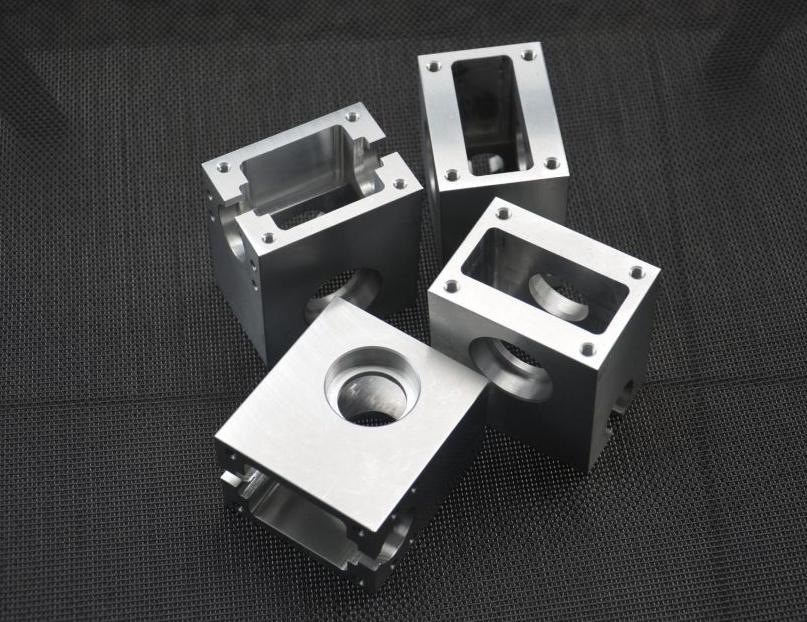
Metal in CNC Milling
Metals have long been the material of choice in CNC milling due to their exceptional strength, durability, and thermal stability. Metal materials, such as aluminum, steel, copper and titanium, are used in CNC milling to manufacture high-precision, high-load mechanical parts due to their high strength, wear resistance and good electrical and thermal conductivity.
Benefits of Using Metal in CNC Milling:
- High Strength and Durability: Metals offer superior mechanical properties, making them ideal for parts that require high strength, wear resistance, and longevity.
- Thermal Stability: Metals maintain their properties under a wide range of temperatures, making them suitable for high-heat applications.
- Precision and Finish: Metals can be machined to extremely tight tolerances, providing high precision and a superior surface finish.
- Wide Range of Alloys: Metals such as aluminum, steel, titanium, and brass offer a broad spectrum of properties, allowing for customization to specific needs.
Challenges of Using Metal in CNC Milling:
- Higher Costs: Metals are generally more expensive than plastics, both in material costs and machining time. The hardness of metals also leads to increased tool wear and maintenance.
- Weight: The heavier nature of metals can be a disadvantage in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in automotive and aerospace design.
- Corrosion Risk: While many metals are prone to corrosion, this can be mitigated through the use of alloys or protective coatings.
Metal remains the go-to material for CNC milling when strength, durability, and precision are paramount. While more expensive and heavier than plastic, metal’s unmatched properties make it essential for demanding applications.

Comparison: When to Choose Plastic vs. Metal
Selecting the right material for CNC milling—plastic or metal—is crucial to achieving the desired performance, cost-efficiency, and durability of the final product. The decision involves evaluating various factors, such as strength, weight, cost, thermal properties, and application-specific requirements. Here is a detailed comparison of plastic and metal:
| Comparison Aspect | When to Choose Plastic | When to Choose Metal |
| Strength and Durability | Suitable for lower stress applications, where flexibility or lower strength is acceptable. | Ideal for high-stress, high-load applications requiring superior strength and durability. |
| Weight Considerations | Best for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in aerospace or portable devices. | Chosen when weight is less of a concern or when added weight contributes to stability and strength. |
| Thermal and Chemical Resistance | Adequate for non-extreme environments, with specific plastic formulations offering good chemical resistance. | Ideal for high-temperature or chemically harsh environments where thermal stability and resistance are needed. |
| Electrical Insulation | Preferred for components requiring electrical insulation, such as circuit boards and electronic housings. | Not typically chosen for insulation; used when electrical conductivity is needed or with insulating layers. |
| Cost Considerations | More cost-effective, especially for large-scale production or projects with tight budgets. | Worth the investment for applications where performance, precision, and longevity justify the higher cost. |
| Precision and Surface Finish | Suitable when high precision is not critical, and cost savings are prioritized over perfect surface finishes. | Best for applications requiring tight tolerances and superior surface finishes, such as in aerospace or medical devices. |
The choice between plastic and metal for CNC milling is determined by the specific demands of your project. If your application requires high strength, durability, and thermal stability, metal is likely the better option. On the other hand, if you need a lightweight, cost-effective, and electrically insulating material, plastic is the preferred choice. By carefully assessing the factors that matter most to your application, you can make an informed decision that ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
If you still not sure the material for your project, please feel free to contact our experts and they will give you reliable suggestions.