CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing technology in which a rotary cutter advances into a metal block or bar to remove material. During this subtractive process, the cutting tool gradually removes material until the workpiece resembles the desired part. The cutter’s speed, pressure, and direction can be adjusted to achieve different effects. It currently does the majority of the work. In general, once the tooling is installed, CNC machining technology provides complete automation free of human error in most cases. This has increased the speed of operations and the complexity of the components handled. When planning a CNC machining project, it is critical to determine how much CNC machining costs. This article investigates the various factors influencing CNC milling costs and offers suggestions for lowering your expenses.

What Are the Factors That Affect the Cost of CNC Milling and Machining?
The common factors that affect the overall cost of CNC milling are outlined below:
| Number of Axes | The number of axes determines the complexity of the parts that CNC machining can make. Although multi-axis machining provides greater manufacturing freedom and capabilities, using 5-axis and 6-axis machines significantly raises the cost of a project. |
| Part geometry | This refers to the dimensions of a part. The larger a part, the more material is required to manufacture it, and thus the higher the cost. |
| Milling Time | Machines that produce parts more quickly necessitate special robotics in the CNC mechanism. As a result, startup costs are higher. As a result of improved time utilization, the overall cost of CNC machining is lower. |
| Cutting Tolerances | A tighter tolerance yields greater accuracy in the finished product. However, a high-quality machine capable of cutting precisely to tighter tolerances as part of the manufacturing process will be more expensive. |
| Quantity of parts | The number of parts ordered for a machine affects its overall cost. This is because large orders are expensive; however, the more parts there are, the less each additional unit costs. This means that large orders increase the final cost of the part while decreasing the cost per unit. |
| Tooling | Tooling costs can account for a significant portion of CNC machining projects. While some tools, such as dies and clamps, can be reused multiple times, others, such as cutting tools, are consumable. |
| Raw Material Cost | The cost of raw materials is a critical factor in any CNC machining project. These costs cannot be eliminated, but they can be optimized. Aside from the quantity, the type of raw material plays an important role in determining raw material costs. |
| Labor Costs | The purpose of CNC machining is to eliminate the labor cost in manual processes like turning, moving, or operating the cutters. However, there are still some labor costs in changing tools, setting up the workpiece, and, most importantly, the operator’s salary. |
| Custom CNC Machining | In many cases, CNC machining custom parts can require non-standard tools, custom materials or sizes, or specialist CNC milling machines. For these projects, the pricing can be significantly higher. |
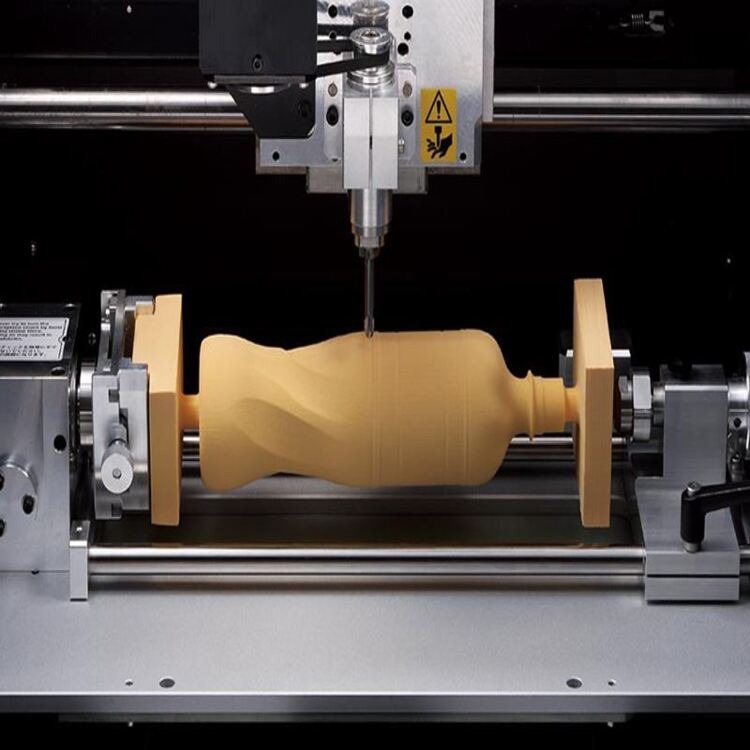

Tips to Reduce CNC Milling Costs
Apart from the initial CNC machine cost, other elements, such as the cost of raw materials and electricity, need to be considered. However, there are some tips you can implement to make the total cost significantly cheaper.
Reduce the Use of Tight Tolerances
This refers to how closely the physical part must match the submitted design. It is typically measured in hundredth or thousandths of an inch. Due to its complexity and demand, a part with unnecessarily tight tolerances increases its overall cost. Tight tolerances necessitate a slower milling process. Not only that, but they require a higher quality CNC machine. This results in increased equipment costs and higher labor costs because the operator’s salary will be higher due to long hours.
Avoiding Multiple Finishes
To achieve a high post-processing finish, CNC machines must spend a significant amount of time on the product to produce higher-quality edges. This increases machine and labor costs, as well as tool wear. Therefore, avoiding multiple product finishes is a good idea. Many products go through secondary finishing processes, which increase completion costs. Using the final CNC-milled product as the finished product is the less expensive option.
Avoid Deep Pockets
Deep pockets refer to situations in which an extended tool reach is required to create deep cavities in the workpiece. Deep pockets created with CNC milling machines cause a variety of issues, including tool breaking, faster tool wear, tool chatter, tool deflection, wall chatter, coolant delivery, chip retrieval, and more. All of these issues result in more frequent tool replacements and workpiece breakage, which increases costs significantly.

Reducing Design Complexity
High design complexity means higher design costs and CNC machining costs. In most cases, a complex design necessitates the use of CNC milling machines with more axes, which can double or triple the overall cost. Most complex designs can be broken down into two or more simpler designs, which are then milled by 3-axis CNC machines. Assembly of these simple designs can result in a complex product. This significantly reduces the cost of CNC machining.
Limiting Length of Threads
When milling screws and bolts, some manufacturers prefer longer threads due to their increased strength. However, in many cases, the extra length is unnecessary, and a shorter thread will do. Longer threads result in a longer CNC process, higher material costs, and wasted resources with no added benefit.
Optimization of Design
Optimizing the design will result in machines taking the shortest routes and cutting the least amount of material required to produce the final product. This leads to more efficient use of time and raw materials. Consulting with an experienced machinist or engineer during the design phase may increase the project’s initial cost, but it will save much more in the end. This is especially true for larger production runs. Investing more in design process planning is recommended for long-term CNC machining cost savings.
Increasing Production Volume
One of the best and simplest ways to cut CNC machining costs is to increase production volume. When volume increases, the process’s fixed costs are distributed across a large number of CNC machined parts. This significantly reduces the manufacturing cost per part. One of the most significant advantages of large production runs is the lower design costs for CNC machined parts. One design blueprint will be used to create 100, 1,000, or 10,000 parts. This results in lower machining costs per product.
Outsource to a Trusted Manufacturer
There are many options when it comes to CNC machining companies. However, a good one will not be the cheapest, but it will provide you with the best value for money and results. To solve the price vs. quality issue, find a trusted manufacturer such as JTR which provides cnc machining services in China and can deliver the quality and price you need.

Conclusion
CNC machining provides incredible versatility and precision, but understanding the costs upfront is critical for making informed decisions. You can accurately estimate and potentially reduce project costs by taking into account factors such as material selection, part complexity, and machining time. Fortunately, there are ways to maximize your CNC milling budget. Simplifying part design, using standard materials and finishes, and working with manufacturers who provide CNC milling service early in the process can all result in significant savings. Remember that the ideal CNC milling partner does more than just offer competitive rates; they also provide expertise to help you find cost-effective solutions. By prioritizing these considerations, you can maximize the benefits of CNC machining while keeping your project financially viable.