Plastic processing is a general term for various processes that convert synthetic resins or plastics into plastic products and is the largest production sector in the plastics industry. Plastic processing generally includes the compounding, forming, machining, joining, trimming, and assembly of plastics. The last four processes are carried out after the plastic is formed into finished or semi-finished products, also known as secondary plastic processing.

Many plastic processing technologies are borrowed from rubber, metal and ceramic processing. The history of plastic processing dates back to the 1890s. In the early stage of plastic processing technology, because plastic materials are flammable, they can only be made into blocks by molding, and then machined into sheets. Conventional plastic sheets can be processed by thermoforming.
With the development of technology, more molding technologies are applied to the processing and manufacturing of plastic parts. Among them, casting molding was successfully researched with the advent of phenolic resin; injection molding began in the 1920s and was used to process cellulose acetate and polystyrene; in the mid-1930s, soft polyvinyl chloride extrusion molding was successfully developed, special for plastics The single-screw extruder came out accordingly; in 1938 the twin-screw extruder was also put into production.
In the 1980s, plastic processing developed in the direction of high efficiency, high speed, high precision, energy saving, large-scale or ultra-small and ultra-thin. With the entry of computer technology into this field, the entire plastic processing technology has been raised to a new level.
Top 9 Plastic Processing Solutions
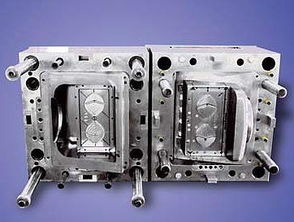
1. Injection Molding
Injection molding is a method of producing shapes for industrial products. Products are usually injection molded using rubber or plastic. Injection molding can also be divided into injection molding and die casting. An injection molding machine (referred to as an injection machine or injection molding machine) is the main molding equipment for making thermoplastics or thermosets into various shapes of plastic products using plastic molding molds. Injection molding is achieved by injection molding machines and molds.
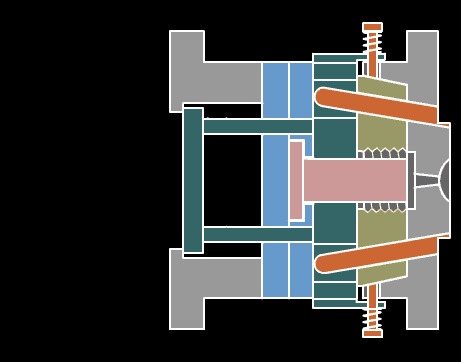
2. Extrusion
This method is a processing method in which the material passes through the action between the extruder barrel and the screw, while being heated and plasticized, it is pushed forward by the screw, and continuously passes through the head to make various cross-sectional products or semi-products.
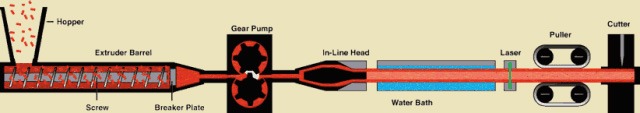
3. Rotational Moulding
Rotational Moulding is to add the metered plastic (liquid or powder) into the mold first, after the mold is closed, make it rotate along two vertical rotation axes, while heating the mold, the plastic material in the mold is under the action of gravity and thermal energy. , gradually and evenly coat, melt and adhere to the entire surface of the cavity, form the same shape as the cavity, and then cool, shape, and demold to obtain products of the desired shape.

4. Blow Molding
Blow molding is a rapidly developing plastic processing method.
It refers to a tubular plastic parison obtained by extrusion or injection molding of thermoplastic resin, which is placed in a split mold while hot (or heated to a softened state). Immediately after the mold is closed, compressed air is introduced into the parison, so that the plastic parison is inflated and adhered to the inner wall of the mold. Finally, after cooling and demoulding, various plastic products with hollow in the middle are obtained.
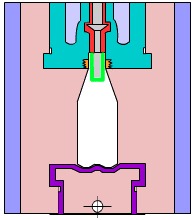
5. Compression Molding
Compression molding is a process in which powder, granular or fibrous plastics are first put into a mold cavity at a molding temperature, and then closed and pressed to form and solidify. Compression molding can be used for thermosets, thermoplastics, and rubber materials.
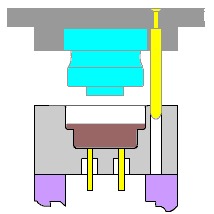
6. Foaming
Foaming is the process of adding appropriate foaming agents to foamed materials (PVC, PE, PS, etc.) to make plastics have a micro cellular structure. In industrial production, almost all thermosetting and thermoplastic plastics can be made into foamed plastics, and foam molding has now become a very important processing method in plastics processing.
According to the cell structure, foam plastics can be divided into two categories:
If most of the pores are connected, it is called open-cell foam; if most of the pores are separated from each other, it is called closed-cell foam.
The open or closed-cell foam structure is determined by the manufacturing method.
(1) Chemical foaming The gas generated by the thermal decomposition of the specially added chemical foaming agent or the chemical reaction between the raw material components makes the plastic melt and fill the cells.
The gases released by the chemical foaming agent during heating include carbon dioxide, nitrogen, ammonia, etc.
Chemical foaming is commonly used in the production of polyurethane foam.
(2) Physical foaming is a method of dissolving gas or liquid in plastic and then expanding or vaporizing it. There are many types of plastics suitable for physical foaming.
(3) Mechanical foaming is a foaming method in which the gas is mixed into the liquid mixture by mechanical stirring, and then cells are formed through the shaping process. This method is commonly used in urea-formaldehyde resins, and others such as polyvinyl formal, polyvinyl acetate, and polyvinyl chloride sol are also applicable.
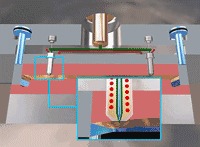
7. Laser Rapid Prototyping (SLS 3D Printing Technology)
A new manufacturing technology that integrates advanced technologies such as CAD, CAM, CNC, laser, precision servo drives, and new materials.
Compared with traditional manufacturing methods, it has the following features: high reproducibility and interchangeability of prototypes; the manufacturing process has nothing to do with the geometry of the prototype; the processing cycle is short, the cost is low, and the general manufacturing cost is reduced by 50%, and the processing cycle is shortened by more than 70%; high Technology integration to realize the integration of design and manufacture.
It can not only form a variety of hot-melt plastic products but also can be used to form various metal materials. It is a processing method that has developed rapidly in recent years. It is widely used in the manufacture of new products and the medical and aerospace fields with very few mass production quantities.
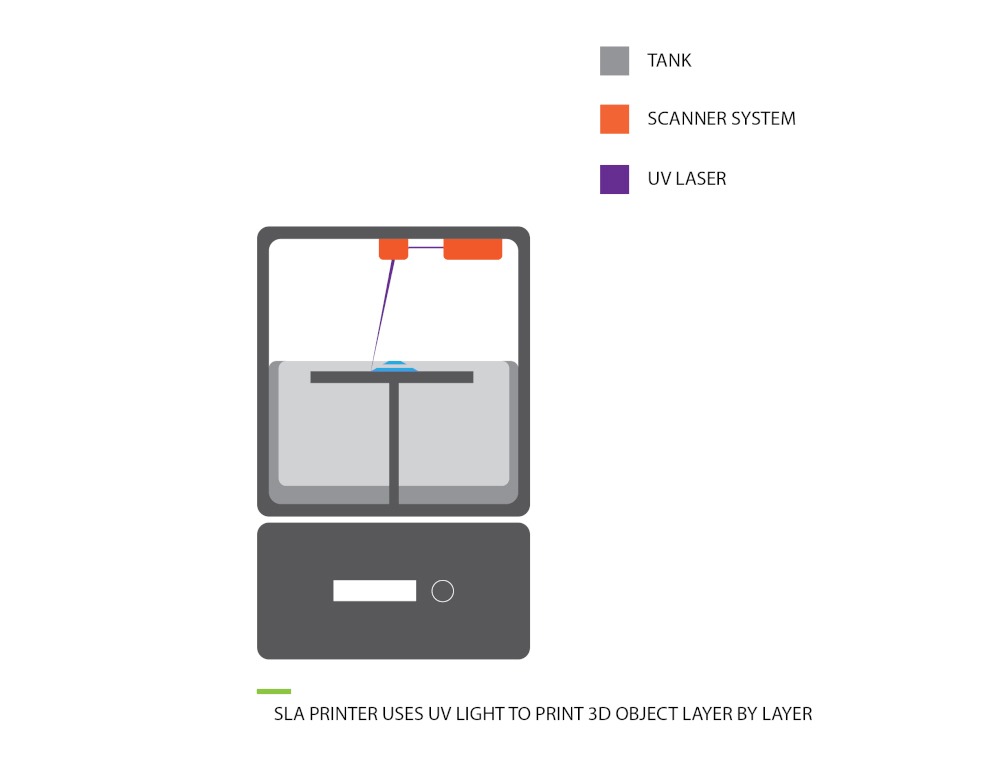
8. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM 3D Printing Technology)
Fused Deposition Modeling is the process of extruding a filament of filamentary material such as thermoplastic, wax, or metal from a heated nozzle, followed by a predetermined trajectory for each layer of the part, at a fixed rate.

This process is very simple, and the fused deposition printer equipment can be reduced to the size of a shoebox, which is suitable for family and popular science education. It is the 3D printing technology with the highest output and popularity.
9. CNC Machining Process (Referred to as CNC)
CNC machining is a process of machining products through automated machine tools equipped with a program-controlled system.
The control system can logically process the program specified by the control code or other symbolic instructions, and decode it, to make the machine tool move and process the parts.
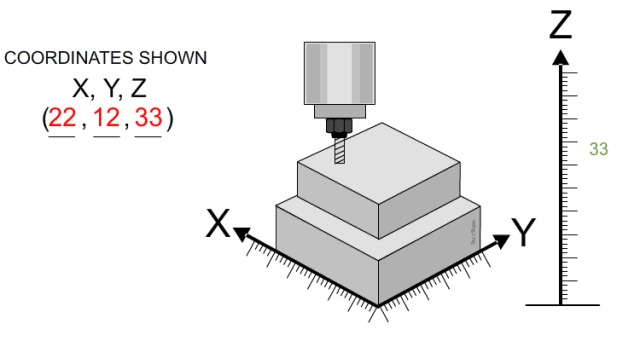
3D printing is to process products by stacking layers, similar to building a house. In principle, it is a processing method of layer-by-layer addition. CNC is the exact opposite of subtractive machining. The final part is obtained by cutting off unwanted parts from a solid object.
As a professional CNC processing and plastic parts processing supplier in China, JTR has been solving the processing problems of plastic parts for customers all over the world. Our engineers will choose better processing methods for customers (eg: CNC processing, injection molding, 3D printing). You no longer need to worry about how to produce cheap and high-quality plastic parts.
If you have any processing questions, please contact us, we will be your best processing manufacturer.