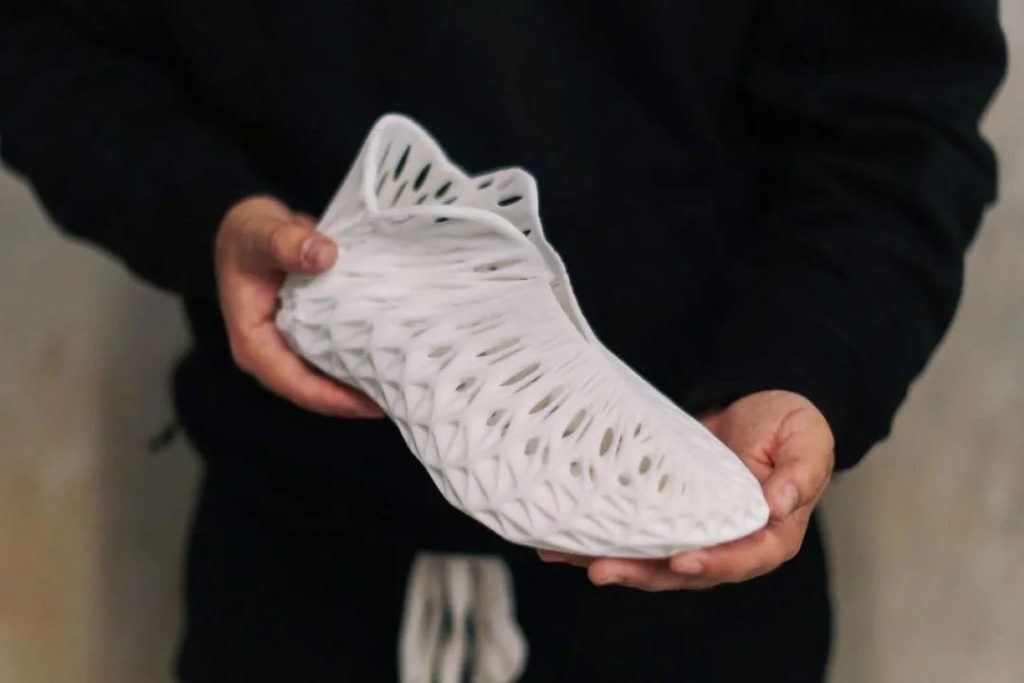
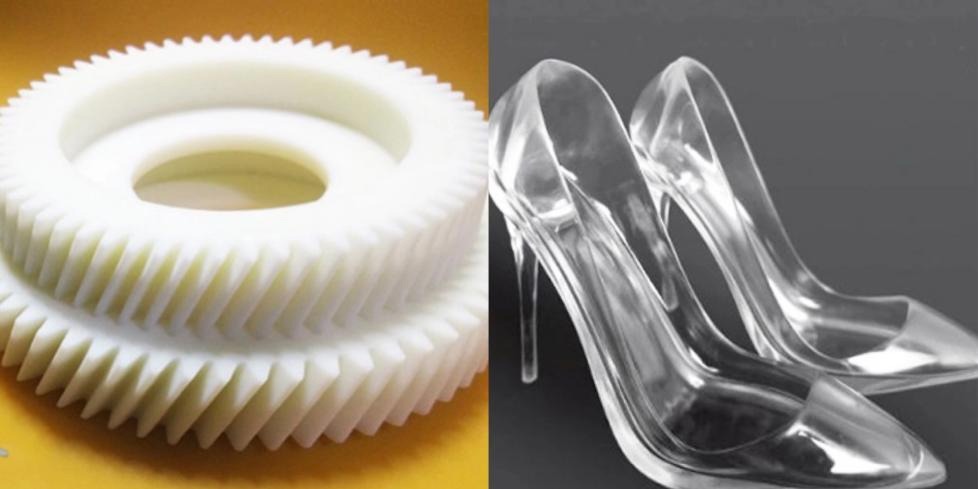
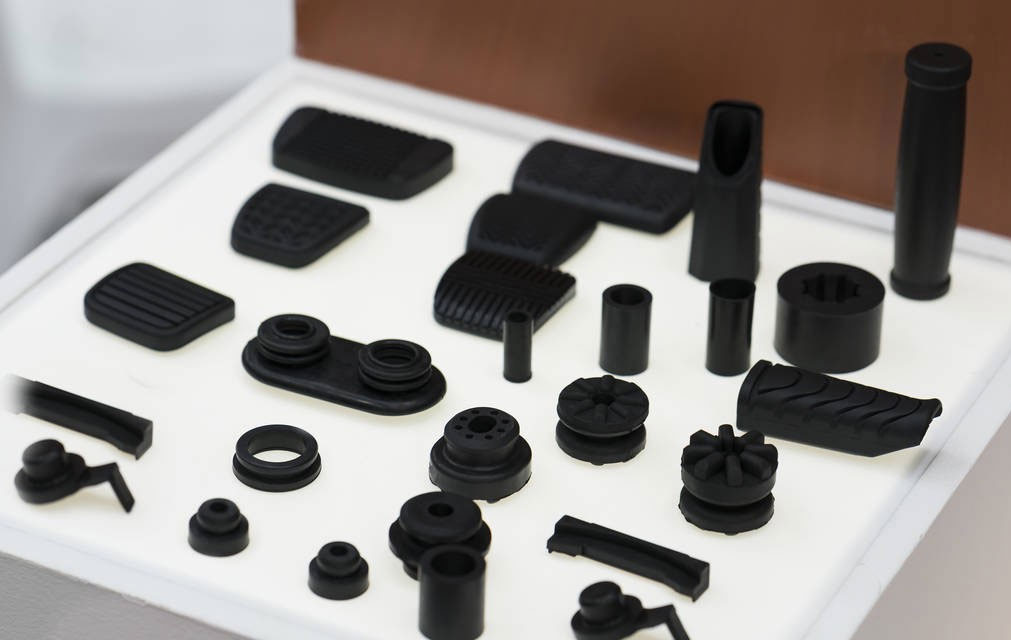
3D printing seems to have faded out of sight. Due to the limitations of 3D printing materials and the inability to mass-produce the same product, 3D printing is considered more suitable for custom machining of parts.
However, due to the continuous updating of 3D printing technology, 3D printing has more possibilities in the field of parts manufacturing in the industrial field – such as “FDM 3D printing“. The continuous improvement of this technology has led to the fact that people can now complete the production of metal products in batches through FDM.

What is FDM 3D printing?
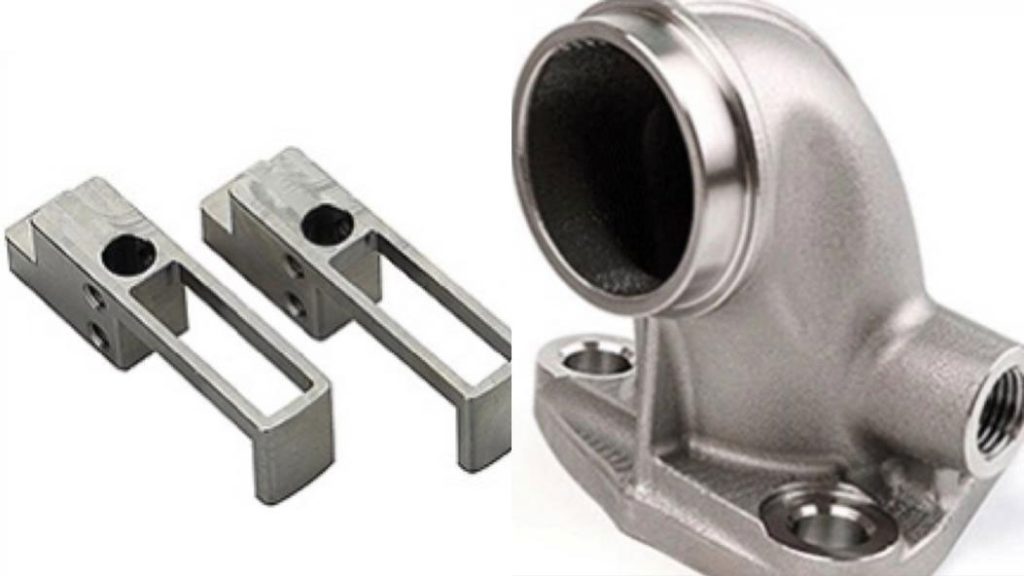
FDM metal forming technology is developed based on metal injection molding (MIM) technology. MIM is a brand-new component processing technology formed by introducing plastic injection molding technology into the field of powder metallurgy.
The basic process steps of metal injection molding are: first select the metal powder and binder required by composite MIM, then use an appropriate method to mix the powder and binder into a uniform feed at a specific temperature, and then granulate after injection molding. After obtaining the formed blank, degreasing treatment is performed, and finally, the blank is subjected to degreasing treatment, and finally, the blank is sintered and densified to obtain the final formed product.
Fused deposition modeling metal 3D printing is a 3D printing technology that combines the MIM process and is similar to FDM. Unlike FDM plastic forming, the material used in FDM metal forming is wire. Unlike common SLM, this metal 3D printing method does not use lasers in the forming process, nor does it use powders.

How does FDM 3D printing turn metal powders into products?
FDM 3D printing works in a similar way to MIM, as mentioned above.
- Brushed
The metal powder (such as stainless steel) is thoroughly mixed with the binding material, and the wire is obtained by drawing.
- Printing and forming
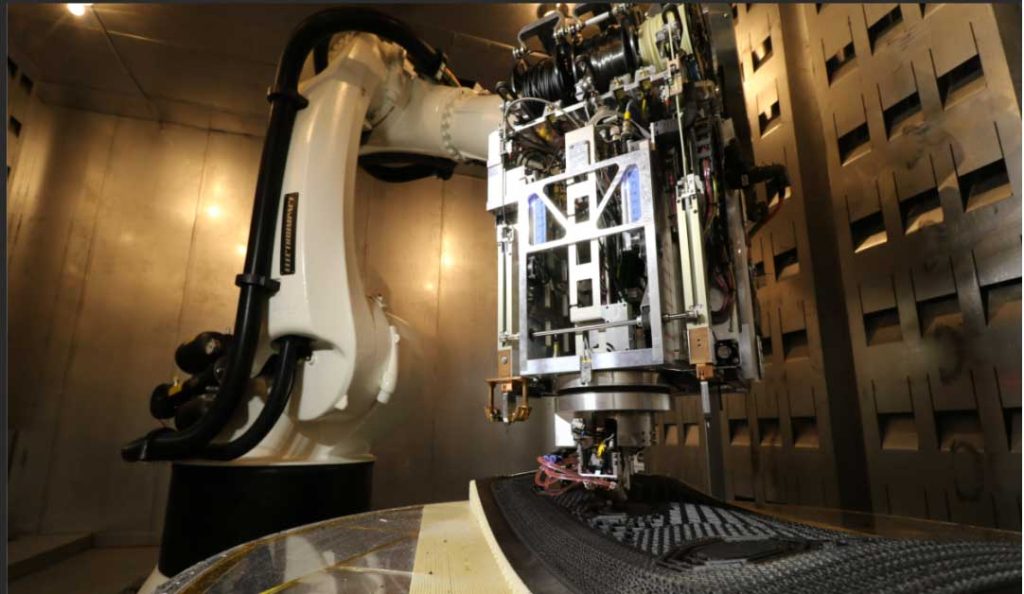
Use FDM equipment high temperature (above 300 ℃) nozzle to melt the wire, spray it out, and form it layer by layer to obtain a preliminary metal part. The nozzle needs to have high strength and high wear resistance because the metal mixture can easily wear the nozzle; if a brass nozzle is used, a new nozzle is required to print a roll.
- Degreasing
Heat the metal part, degrease it, and evaporate most of the bonding material (the part will shrink at this point).
- Sintering
High-temperature sintering removes all bonding material and the part shrinks further. The size of the sintered metal parts shrinks by 15%~17% compared with the metal parts just printed (the binder material evaporates, the gap between the powders is reduced, and the parts become denser), and the quality is reduced by 20%.
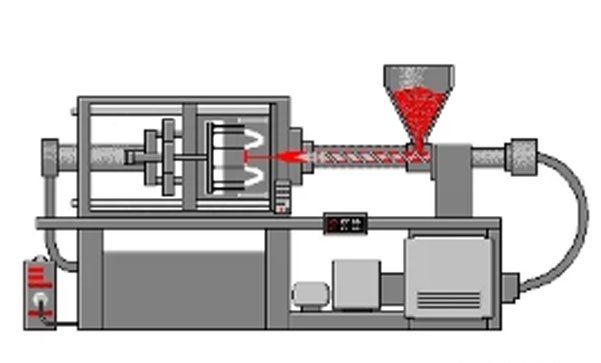
What are the new advantages of FDM 3D printing in the manufacturing field in 2022?
Compared with consumer-grade and professional-grade FDM equipment, industrial-grade FDM equipment now adds a constant temperature chamber and high-temperature nozzle, and the temperature of the printing chamber can even reach 300°C.
FDM 3D printers can be used to print high-performance materials such as PEEK, PEKK, ULTEM, PEI, etc., and meet the application-end requirements for high-temperature resistant, anti-corrosion, and high-impact materials, as well as industrial grades such as large size and high efficiency.
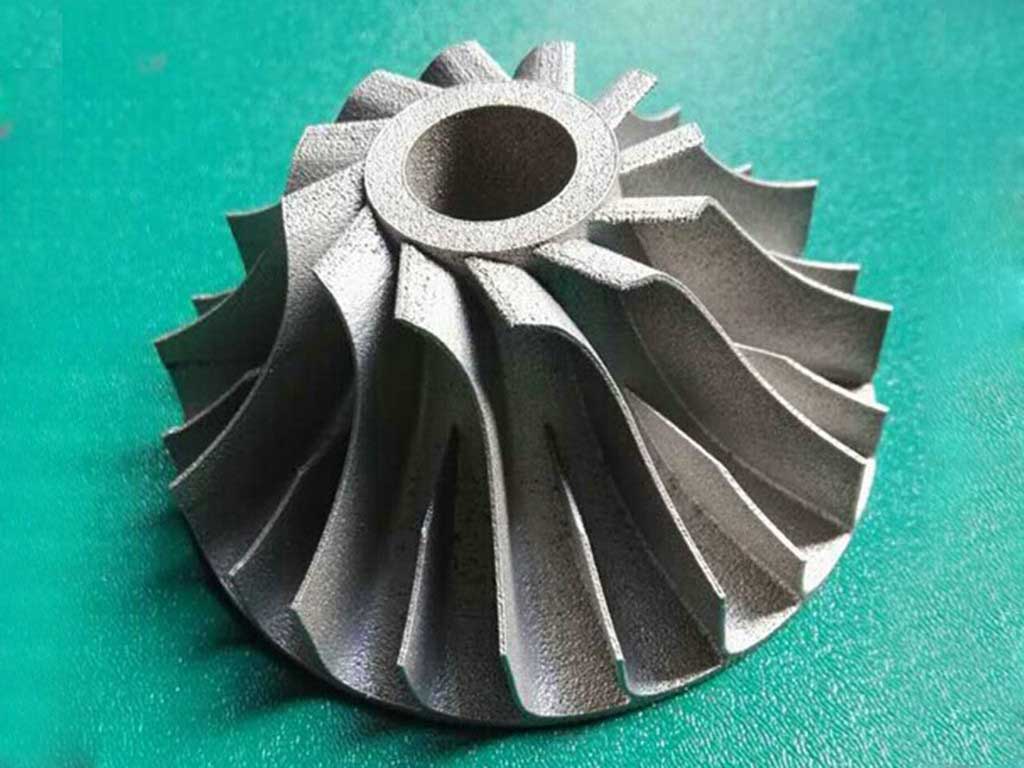
Using FDM technology combined with the MIM process, which is like Desktop Metal’s solution, directly prints metal injection materials, then cleans, sinters, and finally produces metal parts.
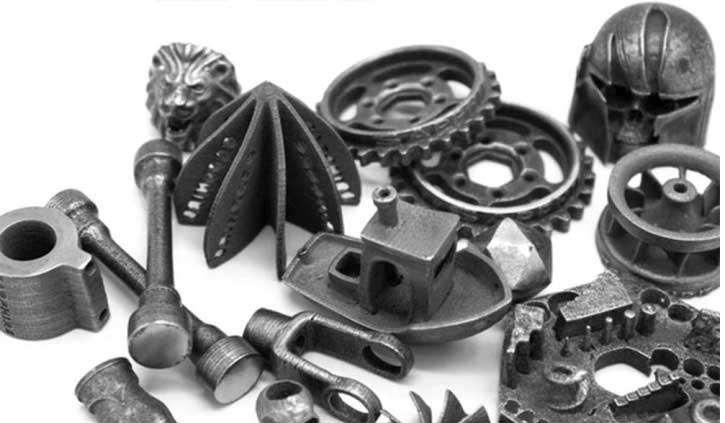
Whether it is casting or metal injection molding, it combines traditional technology, materials, and FDM technology, so FDM technology can be used for the production and processing of metal parts, and its advantages are more flexible hardware and lower cost.
Therefore, 3D printing is not impossible to complete high-intensity industrial production tasks like the previous two years, but can fully realize the production of parts or products.