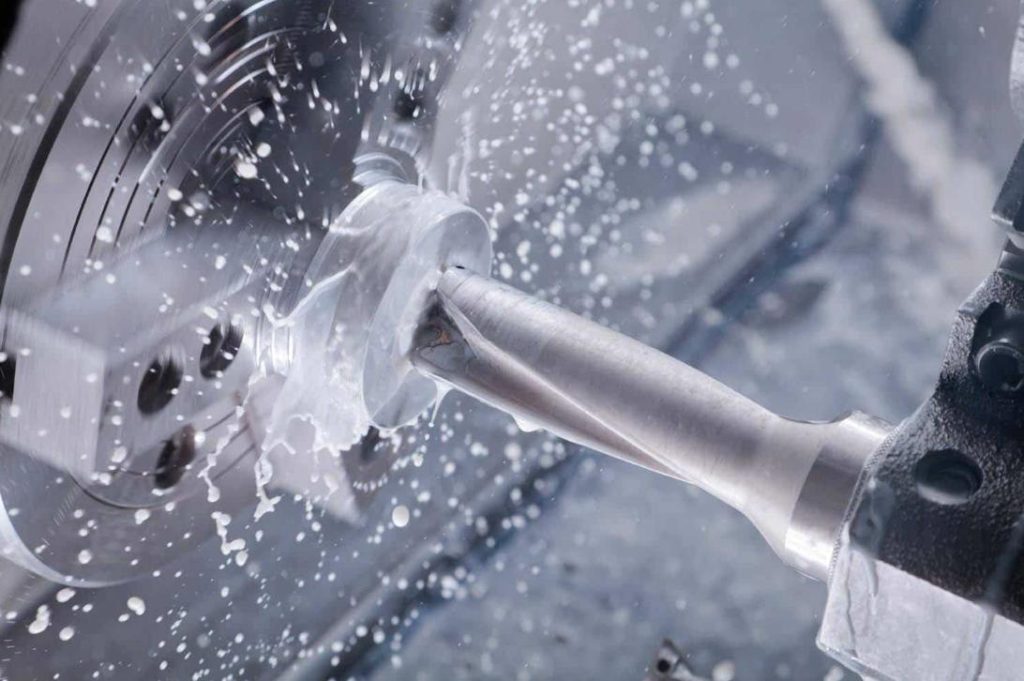
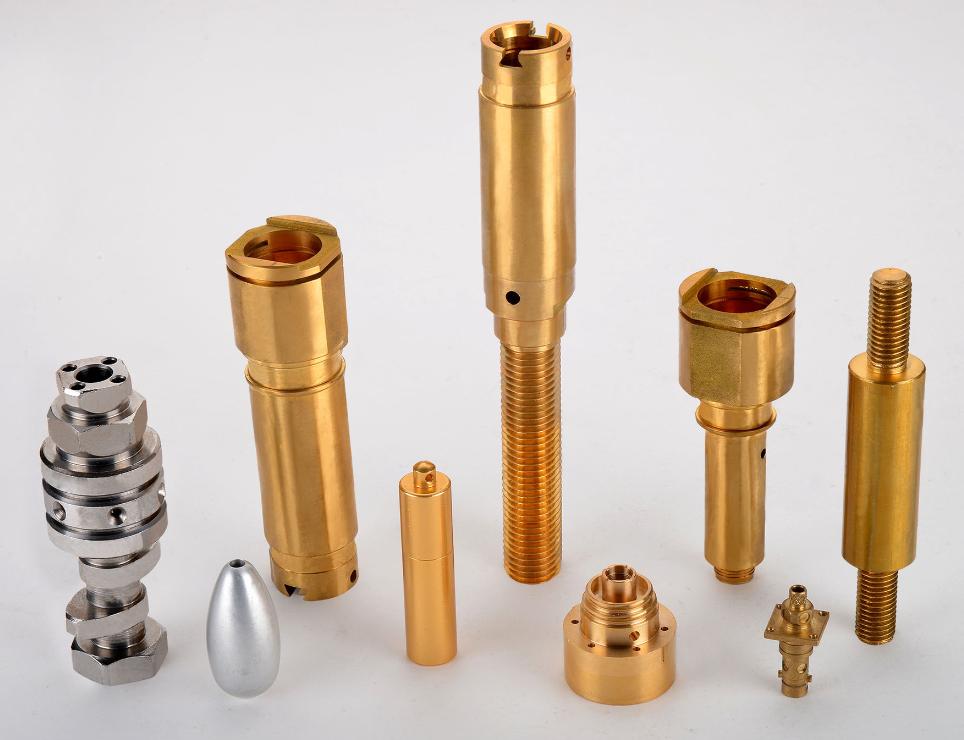
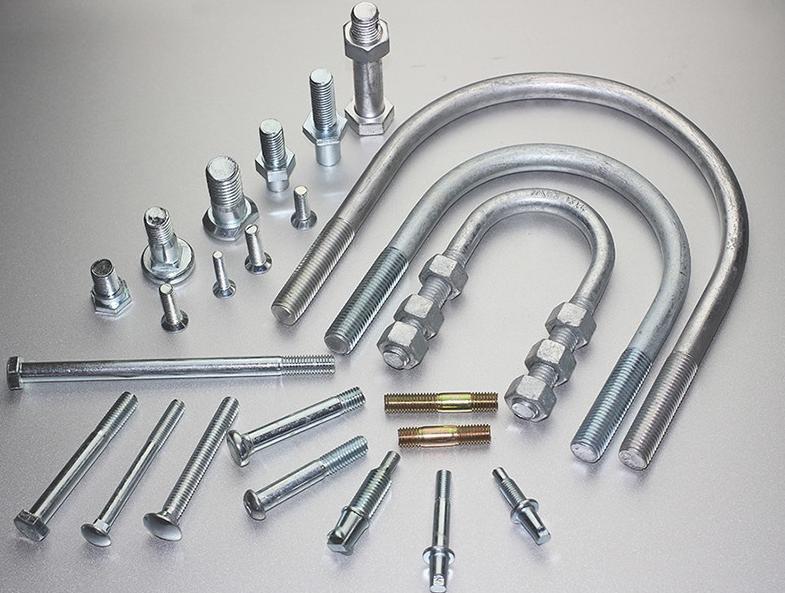
The food processing industry relies heavily on specialized machinery to efficiently transform raw ingredients into finished products. From simple mixers to complex automated lines, these machines are composed of numerous interconnected parts. The selection and maintenance of these parts are crucial for ensuring optimal equipment performance, product quality, and food safety. Here we will look into the key aspects of selecting and maintaining food processing machinery parts, then give you some tips for cost-effective management.
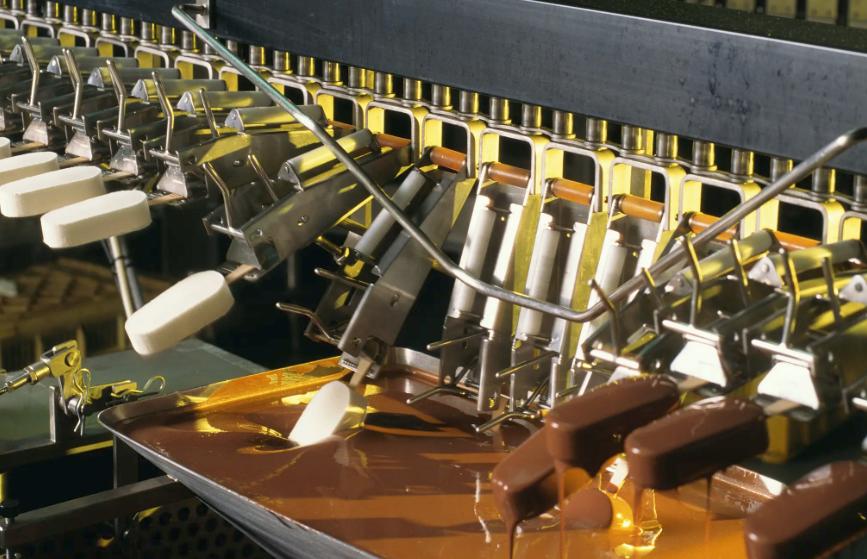

What Are Food Machinery Parts?
Food machinery parts are the components that make up the intricate systems within food processing equipment. These parts include blades, belts, motors, seals, bearings, sensors, nozzles, and more. Each part has a specific function, such as cutting, conveying, mixing, or ensuring safety protocols.
For instance:
- Blades are used in slicing, dicing, or chopping food products.
- Belts facilitate the smooth transfer of materials between different stages of processing.
- Seals and bearings ensure the machinery operates efficiently without leaks or excessive friction.
These parts must meet stringent standards for durability, hygiene, and compatibility, given their direct or indirect contact with food products. Ensuring the quality and reliability of these parts is essential for maintaining the integrity of the food produced.

Top 3 Factors to Consider When Selecting Machinery Parts
The selection of high-quality machinery parts is paramount for the smooth operation, longevity, and safety of food processing equipment. Here are three critical factors to consider:
1. Material Selection:
The materials used in food processing machinery parts must meet strict food safety standards. Corrosion resistance, wear resistance, food contact safety are key points to be considered.
Corrosion Resistance: The food processing environment is often harsh, with exposure to moisture, chemicals, and aggressive cleaning agents. Choosing materials that resist corrosion is crucial to prevent equipment failure and maintain hygiene.
- Stainless Steel: A widely used material in food processing due to its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and easy cleanability.
- Food-Grade Plastics: Offer good chemical resistance, lightweight properties, and can be easily molded into complex shapes. Examples include high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene (PP), and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
- Corrosion-Resistant Alloys: Such as aluminum alloys and titanium alloys, offer excellent resistance to specific corrosive environments and can be used in specialized applications.
Wear Resistance: Components that experience high levels of friction, such as bearings, gears, and conveyor belts, require materials with excellent wear resistance to minimize wear and tear.
- Hardened Steel: Offers high hardness and durability, making it suitable for high-stress applications.
- Ceramic Materials: Exhibit exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
Food Contact Safety: Materials must comply with stringent food safety regulations, including FDA and USDA guidelines. They must be non-toxic, inert, and free from any substances that could contaminate food products.

2. Precision Requirements:
Precision is essential to ensure machinery functions as intended, particularly in processes requiring exact measurements or fine tolerances.
The level of precision required varies significantly depending on the specific application. For critical components like bearings, gears, and shafts, high precision is essential to ensure smooth operation, minimize friction, and prevent premature wear. Inaccurate parts can lead to misalignment, increased vibration, and reduced equipment efficiency.
Precision is often expressed in terms of tolerances, which define the acceptable range of variation in dimensions and other critical parameters.
Modern manufacturing techniques, such as CNC machining and precision casting, enable the production of parts with extremely high levels of accuracy and consistency.
3. Compatibility:
Compatibility ensures that new parts integrate seamlessly with existing machinery, preventing operational disruptions. Incompatibility can lead to malfunctions, reduced performance, and safety hazards.
Key compatibility considerations include:
- Dimensional compatibility: Ensure that parts have the correct dimensions and fit properly with existing components.
- Interface compatibility: Ensure compatibility with existing interfaces, such as shaft diameters, bolt patterns, and electrical connections.
- System compatibility: Ensure compatibility with the overall control system and automation software.
Using genuine OEM parts or high-quality aftermarket replacements that meet the original specifications is crucial to maintain compatibility and ensure optimal performance.
By carefully considering these factors, food processing businesses can select the right parts to optimize equipment performance, enhance product quality, and ensure the safety and efficiency of their operations.

Maintenance of Food Processing Machinery Parts
Proper maintenance is essential for maximizing the lifespan and performance of food processing machinery. Key maintenance activities include:
Regular Inspections:
Conduct regular visual inspections to identify any signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Check for loose connections, leaks, and unusual noises. Implement a preventative maintenance schedule to proactively address potential issues.
Cleaning and Sanitation:
Maintain strict hygiene standards to prevent contamination and ensure food safety. Clean and sanitize all parts regularly using appropriate cleaning agents and procedures. Follow food safety regulations and guidelines for cleaning and disinfection.
Lubrication:
Properly lubricate moving parts to reduce friction, wear, and tear. Use the appropriate type and amount of lubricant for each component. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and procedures.
Replacement:
Replace worn-out or damaged parts promptly to prevent further damage and equipment failure. Use genuine OEM parts or high-quality aftermarket replacements that meet the original specifications.
Record Keeping:
Maintain accurate records of all maintenance activities, including inspections, cleaning, lubrication, and part replacements. This data can help track equipment performance, identify potential issues, and plan future maintenance.

Tips for Cost-Effective Management
Managing food processing machinery parts effectively can significantly reduce operational costs. Here are some practical tips:
Build Relationships with Reliable Suppliers
Partner with trusted suppliers (like JTR) to ensure access to high-quality parts and prompt service. Negotiate bulk purchasing deals for commonly replaced components.
Stock Critical Spare Parts
Maintain an inventory of essential spare parts to minimize downtime during repairs. Prioritize stocking items with long lead times or frequent replacement needs.
Invest in Quality Parts
Avoid compromising on quality for the sake of cost savings, as inferior parts may lead to higher long-term expenses. Opt for OEM parts when possible for guaranteed compatibility and reliability.
Monitor Usage Patterns
Use data analytics to track the lifespan of parts and identify patterns in wear and tear. Predictive maintenance software can help optimize replacement schedules.
Food processing machinery parts are indispensable for the smooth functioning of equipment in the food industry. Selecting the right components, maintaining them regularly, and managing them efficiently are crucial for ensuring productivity, safety, and cost-effectiveness. By prioritizing quality, precision, and proactive care, businesses can extend the lifespan of their machinery, reduce operational disruptions, and uphold the highest standards of food production.