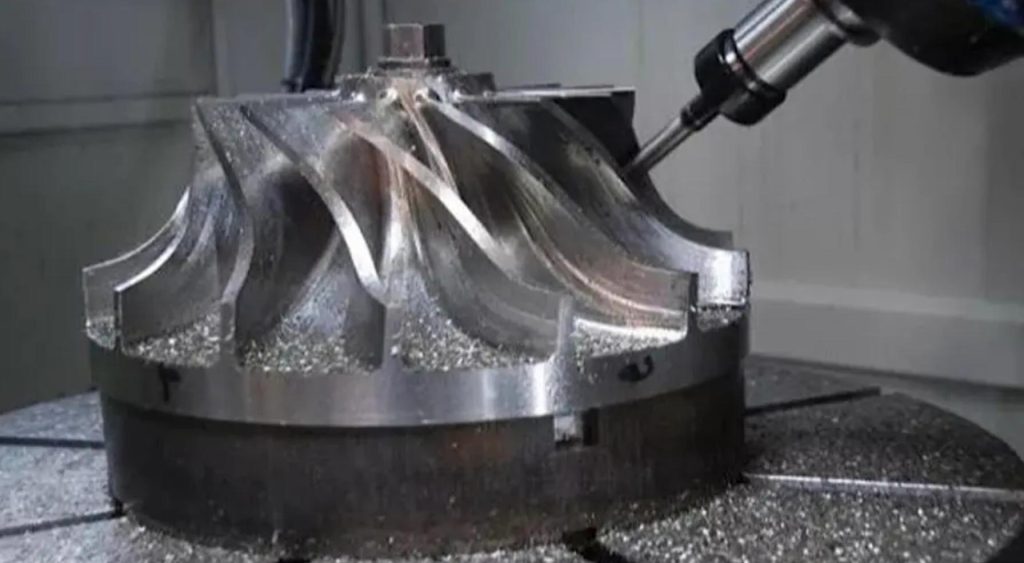
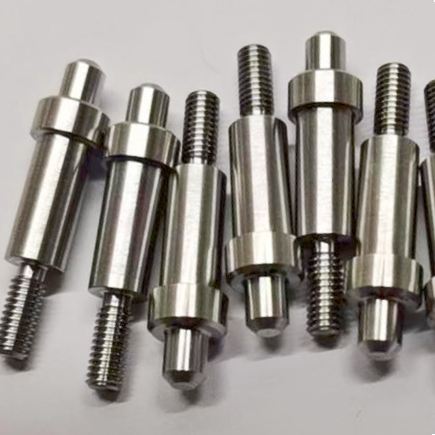
From the tiniest components to the most complex assemblies, every part plays a crucial role in ensuring a vehicle’s performance, safety, and overall quality. To meet the stringent demands of modern automotive engineering, manufacturers have turned to advanced technologies like CNC machining. CNC, or Computer Numerical Control, machining has revolutionized the way automotive parts are produced. By utilizing computer-controlled tools to precisely shape and manipulate materials, CNC machines can create components with unparalleled accuracy and consistency. CNC machining supplier JTR will explore the types of cnc car parts, the intricate processes involved, and the significant benefits it offers in terms of precision, efficiency, and overall product quality.

Common Types of Automotive Small Parts Produced Using CNC Machining
CNC machining is widely used in the automotive industry to produce a vast array of small parts that are essential for vehicle performance and safety. Some of the most common types include:
- Fasteners: Bolts, nuts, screws, and washers are crucial for securing various components throughout the vehicle. They must meet stringent tolerances to ensure proper fit and prevent loosening.
- Gears: Gears transmit power and motion between different components. They require precise machining to maintain gear meshing and prevent excessive wear.
- Bearings: Bearings reduce friction and support rotating components. They need to be manufactured with high accuracy to ensure smooth operation and prevent premature failure.
- Sensors: Sensors monitor various vehicle functions, such as engine temperature, tire pressure, and airbag deployment. They must have precise dimensions and tolerances to provide accurate readings.
- Valve components: Valves control the flow of fluids and gases in the engine. They require intricate machining to ensure proper sealing and performance.
- Fuel system components: Fuel injectors, fuel pumps, and fuel rails are essential for delivering fuel to the engine. They must be manufactured with high precision to avoid fuel leaks and maintain fuel efficiency.
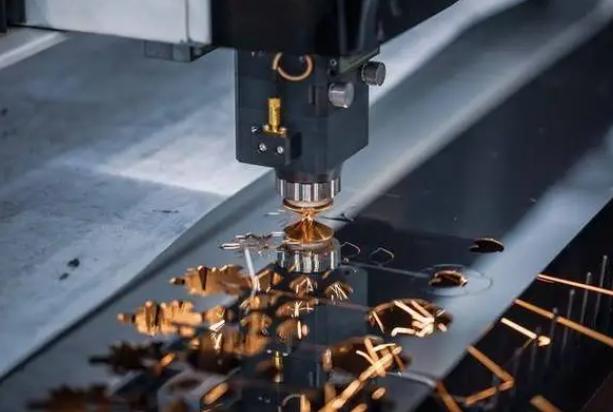

Specific Requirements and Tolerances for Automotive Small Parts
Automotive small parts must meet specific requirements and tolerances to ensure optimal vehicle performance and safety. These requirements often involve:
- Dimensional accuracy: Parts must be manufactured within tight tolerances to fit properly and function as intended. This is especially critical for components that interact with other parts or affect vehicle performance.
- Material selection: The choice of material is crucial for ensuring durability, strength, and corrosion resistance. Factors to consider include the part’s function, operating environment, and cost.
- Surface finish: The surface finish can affect component wear, friction, and appearance. Some cnc car parts may require a smooth finish to reduce drag, while others may need a rough finish for increased grip.
- Heat treatment: Heat treatment processes can improve the mechanical properties of materials, such as hardness and strength. Some parts may require specific heat treatments to meet performance requirements.
- Fatigue resistance: Many cnc car parts are subjected to cyclic loads, which can lead to fatigue failure. They must be designed and manufactured to resist fatigue and prevent premature failure.
- Corrosion resistance: Parts exposed to harsh environments, such as road salt and moisture, must be made from materials that are resistant to corrosion. Coatings or protective treatments may also be necessary.
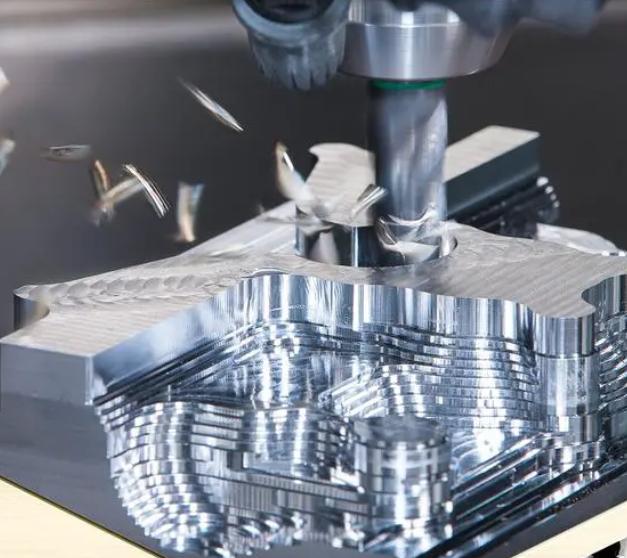
The CNC Machining Process for Automotive Small Parts
1. Design and Programming
Part design: The process begins with creating a detailed 3D CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model of the small part. This model defines the part’s geometry, dimensions, and tolerances.
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) programming: The CAD model is then imported into CAM software, where it is transformed into instructions for the CNC machine. This involves creating toolpaths, which specify the movements of the machine’s tools to produce the desired part.
2. Machining
- Machine setup: The CNC machine is set up with the appropriate tools, fixtures, and workholding devices. The workpiece is securely clamped in place.
- Toolpath execution: The CNC machine follows the toolpaths generated by the CAM software. The tools remove material from the workpiece to create the desired shape and dimensions.
- Machining operations: Various machining operations can be performed, such as milling, drilling, turning, and reaming. The choice of operation depends on the part’s geometry and material.
3. Finishing
- Deburring: After machining, sharp edges and burrs are removed using deburring tools or techniques.
- Inspection: The finished part is inspected to ensure it meets the specified dimensions, tolerances, and quality standards.
- Finishing operations: Additional finishing operations, such as polishing, grinding, or coating, may be required to improve the part’s appearance, surface finish, or corrosion resistance.
4. CNC Software and Toolpath Creation
- CAD/CAM integration: CNC software integrates CAD and CAM functions, allowing designers and engineers to create and modify part designs and generate toolpaths in a single environment.
- Toolpath optimization: The software can optimize toolpaths to minimize machining time, tool wear, and material waste.
- Simulation: Toolpath simulations can be used to visualize the machining process and identify potential problems before the part is actually produced.
- G-code generation: The software generates G-code, which is the programming language used to control the CNC machine’s movements and tool functions.

Benefits of CNC Machining for Automotive Small Parts
CNC machining offers numerous advantages for the production of automotive small parts, contributing to improved efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Some of the key benefits include:
Increased Accuracy and Precision
- Tight tolerances: CNC machines can achieve extremely tight tolerances, ensuring that parts meet precise specifications and fit together seamlessly.
- Consistent quality: The accuracy and precision of CNC machining lead to consistent part quality, reducing the risk of defects and rework.
- Improved performance: Parts produced with high accuracy and precision often exhibit better performance and reliability in automotive applications.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
- Automation: CNC machining is highly automated, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing production efficiency.
- Reduced setup time: CNC machines can quickly switch between different parts, minimizing setup time and maximizing production throughput.
- Increased output: The efficiency of CNC machining allows for higher production volumes, meeting the demands of the automotive industry.
Reduced Waste and Material Costs
- Minimal waste: CNC machining can minimize material waste by precisely cutting parts to the desired dimensions, reducing scrap and rework costs.
- Optimized material usage: CNC software can optimize material usage, ensuring that the maximum amount of material is utilized efficiently.
- Cost savings: Reduced waste and material costs contribute to significant cost savings for automotive manufacturers.
Enhanced Product Quality and Consistency
- Improved reliability: Parts produced using CNC machining are more likely to be reliable and durable, reducing the risk of failures and costly repairs.
- Consistent performance: CNC machining ensures that parts are produced consistently, meeting the high standards required for automotive applications.
- Improved safety: High-quality parts produced with CNC machining can enhance vehicle safety and reduce the risk of accidents.
Greater Design Flexibility and Customization
- Complex geometries: CNC machines can produce parts with complex geometries and intricate details that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods.
- Customization: CNC machining allows for greater customization of parts, enabling manufacturers to meet specific requirements and differentiate their products.
- Rapid prototyping: CNC machining can be used for rapid prototyping, allowing engineers to quickly test and refine designs before final production.
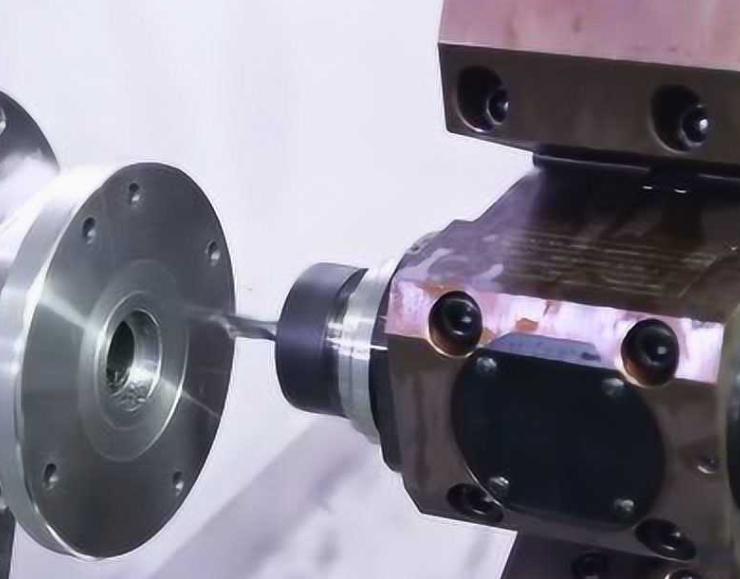

CNC Machining: Driving Automotive Precision
CNC machining has emerged as a cornerstone of modern automotive manufacturing, enabling the production of high-precision small parts that are essential for vehicle performance and reliability. By leveraging the power of computer-controlled tools, CNC machines can create components with exceptional accuracy, consistency, and efficiency. If you need some CNC machining services in the development of your automotive business, then be sure to choose JTR.
Through its ability to deliver precision, efficiency, and flexibility, CNC machining is poised to shape the future of automotive manufacturing for years to come.