Brass, a versatile alloy composed primarily of copper and zinc, has been widely used in various industries for centuries. Its excellent machinability, durability, and aesthetic appeal make it an ideal material for CNC machining. By understanding the different types of brass available and the key factors to consider when selecting a grade, we can optimize their CNC machining processes and produce high-quality components. This article delves into the common types of brass used in CNC machining, explores the crucial factors to consider when choosing a brass grade, and outlines the primary CNC machining processes employed for brass.
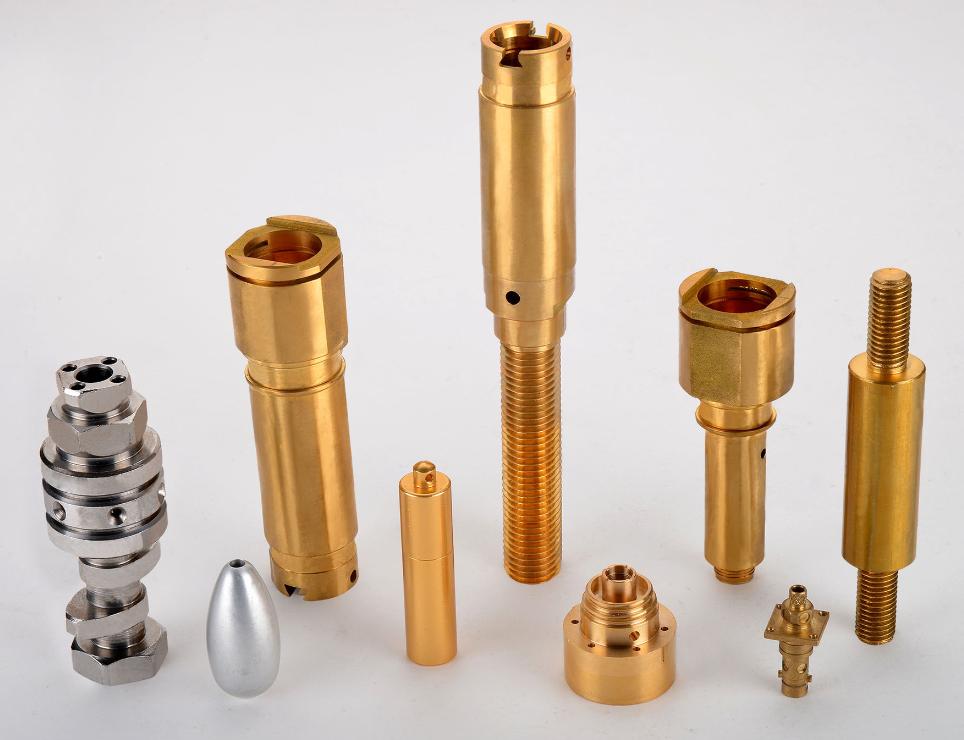

What are the Common Types of Brass Used in CNC Machining?
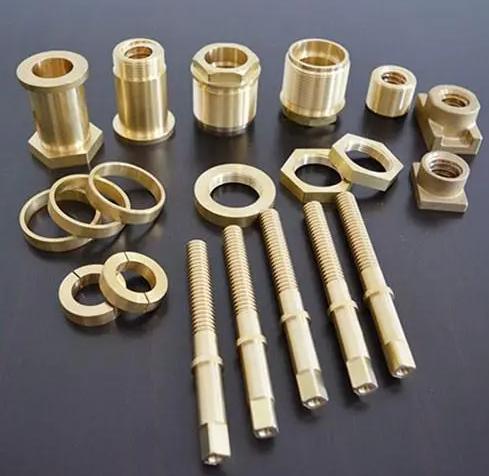
Free-Cutting Brass (C360)
Free-cutting brass, specifically C360, is a highly machinable alloy that excels in CNC operations. Its composition, which includes small amounts of lead, significantly reduces cutting forces and tool wear. This makes it ideal for intricate parts with complex geometries, such as gears, bearings, and electronic components. The smooth cutting action and superior chip evacuation properties of C360 contribute to high-quality finishes and increased productivity.
Naval Brass (C464)
Renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, naval brass, particularly C464, is widely employed in marine applications. Its high copper content and the addition of tin and lead provide excellent resistance to saltwater and other corrosive environments. This makes it suitable for components exposed to harsh conditions, such as boat fittings, marine hardware, and valve bodies. Naval brass also offers good strength and ductility, enabling it to withstand mechanical stress and vibration.
High-Lead Brass (C353)
High-lead brass, such as C353, is another popular choice for CNC machining, especially for parts that require intricate threading or complex shapes. The high lead content in this alloy further enhances its machinability, reducing cutting forces and improving tool life. This makes it suitable for producing components with fine details and tight tolerances. However, it’s important to note that the high lead content can limit its strength and ductility compared to other brass alloys.
Leaded Brass (C385)
Leaded brass, including C385, is a versatile alloy that offers a good balance of machinability and mechanical properties. The addition of lead improves its machinability, making it suitable for producing a wide range of components, such as screws, nuts, and fasteners. Leaded brass also exhibits good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications. While it may not be as strong as some other brass alloys, it offers a cost-effective solution for many CNC machining applications.

What Factors Should I Consider When Choosing a Brass Grade for CNC Machining?
Selecting the appropriate brass grade for a CNC machining project is crucial to ensure optimal performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Several key factors should be carefully considered:
- Machinability: Machinability is a critical factor, especially for complex parts with intricate details. A highly machinable brass grade, such as free-cutting brass (C360), can significantly reduce machining time and tool wear. This translates to lower production costs and faster turnaround times.
- Corrosion Resistance: If the machined parts are exposed to harsh environments, such as saltwater or industrial chemicals, corrosion resistance is paramount. Naval brass (C464) is an excellent choice for marine applications due to its high copper content and the addition of tin and lead, which provide excellent corrosion resistance.
- Strength and Hardness: The required strength and hardness of the brass grade depend on the specific application. For instance, components subjected to significant mechanical stress, such as gears and bearings, may require a stronger brass alloy. High-strength brass alloys, like those with higher zinc content, can provide the necessary mechanical properties.
- Conductivity: For applications where electrical or thermal conductivity is crucial, such as electrical connectors and heat sinks, high-conductivity brass alloys are ideal. These alloys typically have a higher copper content, which enhances their conductivity properties.
- Cost: The cost of the brass grade and the associated machining costs should be considered. While high-performance brass alloys may offer superior properties, they may also be more expensive. It’s essential to balance the desired properties with the budget constraints of the project.
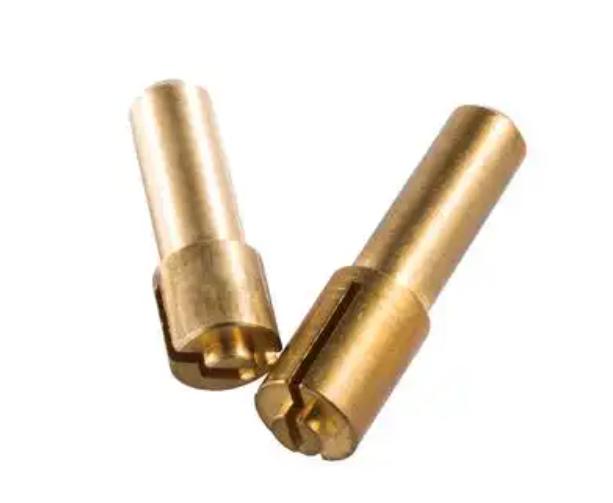

What are the Common CNC Machining Processes for Brass?
Brass is a versatile material that lends itself well to various CNC machining processes. Here are some of the most common techniques used to shape and form brass components:
Milling
Milling is a versatile process that involves removing material from a solid block of brass using rotating cutting tools. CNC milling machines can create intricate shapes, precise features, and complex contours. This process is ideal for producing components such as gears, pulleys, brackets, and custom parts with tight tolerances.
Turning
Turning is a process used to create cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece and using cutting tools to remove material. CNC turning machines can produce a wide range of components, including shafts, bushings, and pins. By utilizing various cutting tools and programming techniques, machinists can create parts with complex threads, tapers, and other features.
Drilling
Drilling is a fundamental process used to create holes of various sizes and depths in brass. CNC drilling machines can accurately position and drill holes with high precision. This process is essential for creating components that require threaded holes, clearance holes, or tapped holes.
Threading
Threading is a process used to create internal and external threads in brass components. CNC machines can perform both internal and external threading operations with high accuracy and efficiency. This is crucial for creating components that require threaded connections, such as screws, nuts, and fittings.
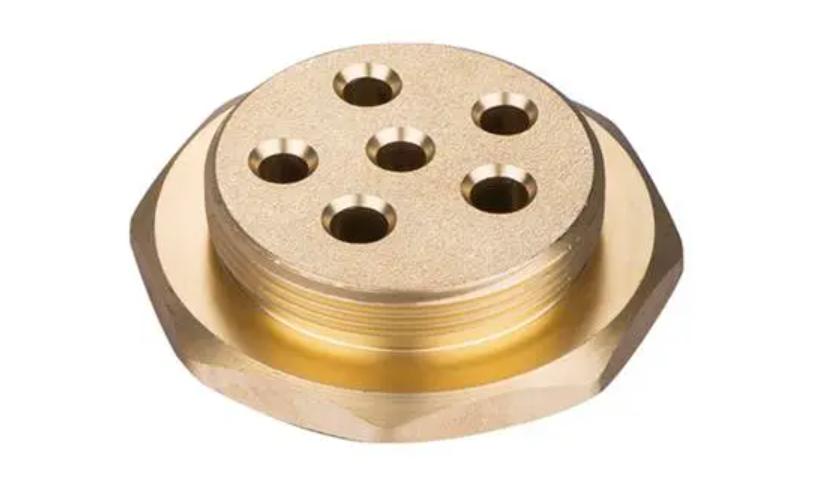

Mastering CNC Machining Brass
Brass, with its diverse range of properties and excellent machinability, continues to be a popular choice for CNC machining. CNC machining service supplier JTR has listed the characteristics of different brass grades and the suitability of various CNC machining processes, so you can produce high-quality, precision-engineered brass components. By carefully considering factors such as machinability, corrosion resistance, strength, conductivity, and cost, you can select the optimal brass grade for your specific application. You can also choose advanced CNC machining techniques, such as milling, turning, drilling, and threading to create intricate and functional brass parts that meet the demands of modern industries.