CNC machining has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, allowing for precise and efficient production of a wide range of components. Among the materials frequently used in CNC machining, brass stands out as a versatile and advantageous choice. Brass offers a multitude of benefits, from its exceptional machinability to its appealing aesthetics and corrosion resistance. In this article, we will delve into the advantages of CNC machining brass and explore the main types of brass alloys commonly utilized in the machining process.
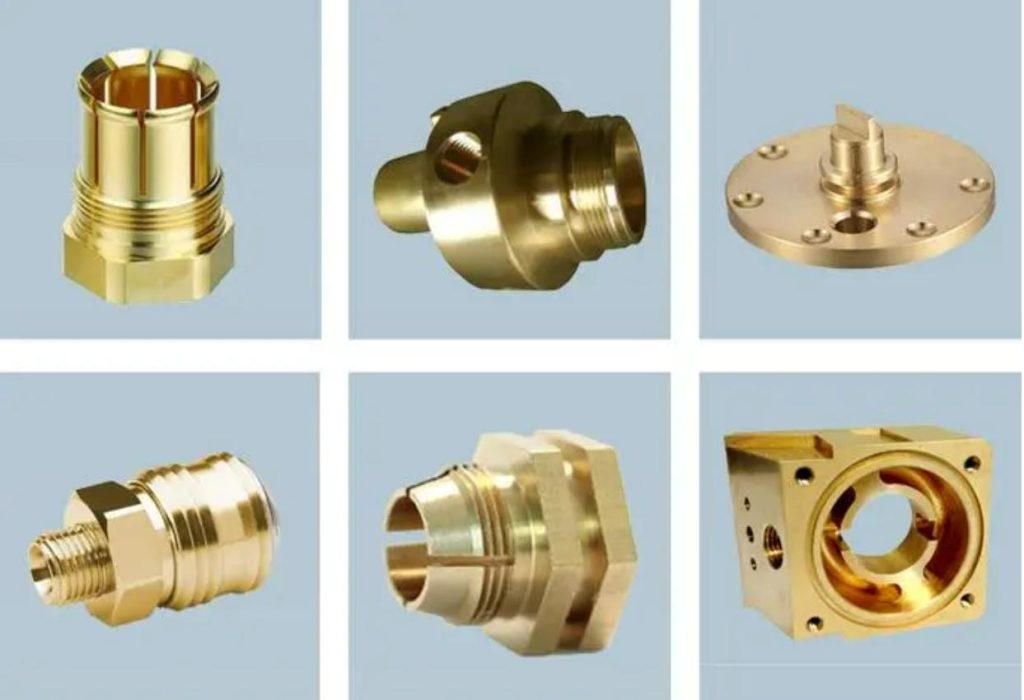

Advantages of CNC Machining Brass
CNC brass offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for various applications. Here are the key advantages of CNC machining brass:
- Excellent Machinability: Brass is known for its exceptional machinability, which makes it well-suited for CNC machining. It has relatively low cutting forces, resulting in reduced tool wear and longer tool life. This allows for efficient and cost-effective machining processes with improved productivity.
- Wide Range of Applications: CNC machining brass is suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries. Its versatility allows it to be used in precision components, electrical connectors, plumbing fittings, decorative elements, architectural hardware, and more. The ability to tailor the alloy composition further expands the range of applications where brass can be utilized.
- Attractive Aesthetics: Brass has a distinctive golden appearance that is aesthetically pleasing. It provides a classic and elegant look, making it desirable for decorative and ornamental applications. CNC machining brass allows for precise shaping and detailing, resulting in high-quality and visually appealing finished parts.
- Corrosion Resistance: Brass exhibits good corrosion resistance, particularly in non-aggressive environments. It can withstand exposure to moisture, air, and certain chemicals without significant degradation. This property makes CNC machined brass parts suitable for applications where corrosion resistance is essential, such as plumbing systems or marine environments.
- Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Brass possesses excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It efficiently dissipates heat during machining operations, reducing the risk of thermal damage to both the workpiece and cutting tools. The high electrical conductivity of brass makes it useful in applications involving electrical components or conductive pathways.
- Availability and Cost-effectiveness: Brass is widely available and relatively cost-effective compared to other metals used in CNC machining, such as stainless steel or exotic alloys. The accessibility and affordability of brass make it a preferred choice for manufacturers looking for a balance between performance and cost.
- Recycling and Sustainability: Brass is a recyclable material, allowing for sustainable manufacturing practices. CNC machining brass parts can be easily recycled and reused, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. The recyclability of brass contributes to a circular economy and resource conservation.
When considering the advantages of CNC machining brass, it is important to also be aware of the specific challenges and considerations associated with the material, such as proper tool selection, cutting parameters, and workpiece design. Adhering to best practices and leveraging the expertise of CNC machining professionals can help maximize the benefits of machining brass.
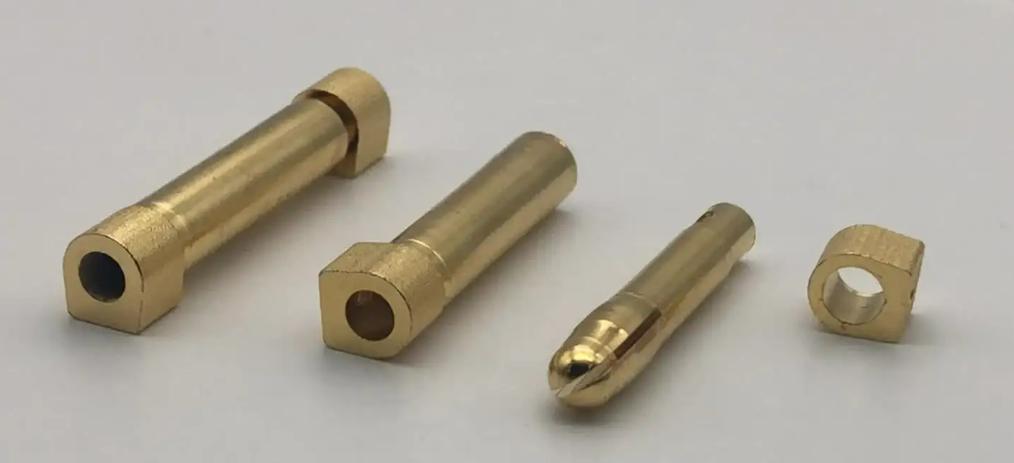

Types of CNC Machining Brass
In CNC machining, various types of brass alloys are commonly used based on their specific compositions and properties. Here are some of the types of CNC machining brass:
- Alpha Brass: Alpha brass, also known as 200 series brass, is a general-purpose brass alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc. It offers good ductility, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Alpha brass is widely used in CNC machining for various applications.
- Alpha-Beta Brass: Alpha-beta brass, also referred to as 300 series brass, is an alloy that contains copper, zinc, and small amounts of other elements such as tin or lead. This alloy provides a balance between strength, ductility, and machinability, making it suitable for CNC machining applications that require higher mechanical properties.
- Free-Cutting Brass: Free-cutting brass, often designated as C36000, is a type of brass alloy specifically designed for enhanced machinability. It typically contains a higher percentage of lead (around 2-3%) as a free-machining element. The addition of lead improves chip formation and reduces tool wear during machining processes. Free-cutting brass is commonly used in high-speed machining and for intricate component production.
- Naval Brass: Naval brass, also known as 464 brass or admiralty brass, is a copper-zinc alloy with small additions of tin and sometimes lead. Naval brass exhibits excellent resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for marine applications. It offers good strength, machinability, and resistance to dezincification.
- Dezincification-Resistant Brass: Dezincification-resistant brass, or DZR brass, is an alloy designed to resist dezincification, a form of corrosion that occurs in certain environments. It contains additional elements such as arsenic or aluminum, which improve its corrosion resistance properties. DZR brass is commonly used in plumbing and fluid-handling applications.
- High-Tensile Brass: High-tensile brass is an alloy with higher tensile strength compared to standard brass alloys. It typically contains higher amounts of zinc and may have additional elements like aluminum or manganese. High-tensile brass provides improved mechanical properties, making it suitable for applications that require greater strength.
These are just a few examples of the types of brass alloys used in CNC machining. The selection of a specific brass alloy depends on the requirements of the application, including desired mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Consulting with material suppliers or CNC machining experts can provide further guidance in choosing the most appropriate brass alloy for specific machining needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CNC machining brass presents a host of advantages that make it a preferred material choice for many applications. The exceptional machinability, wide range of applications, attractive aesthetics, corrosion resistance, thermal and electrical conductivity, availability, and cost-effectiveness are among the key advantages that make brass a versatile option for CNC machining projects.
As CNC machining continues to advance, the possibilities for brass applications are expanding. With ongoing developments in cutting tools, machining techniques, and process optimization, the efficiency and precision of CNC machining brass are expected to further improve, opening doors to new opportunities in various industries.