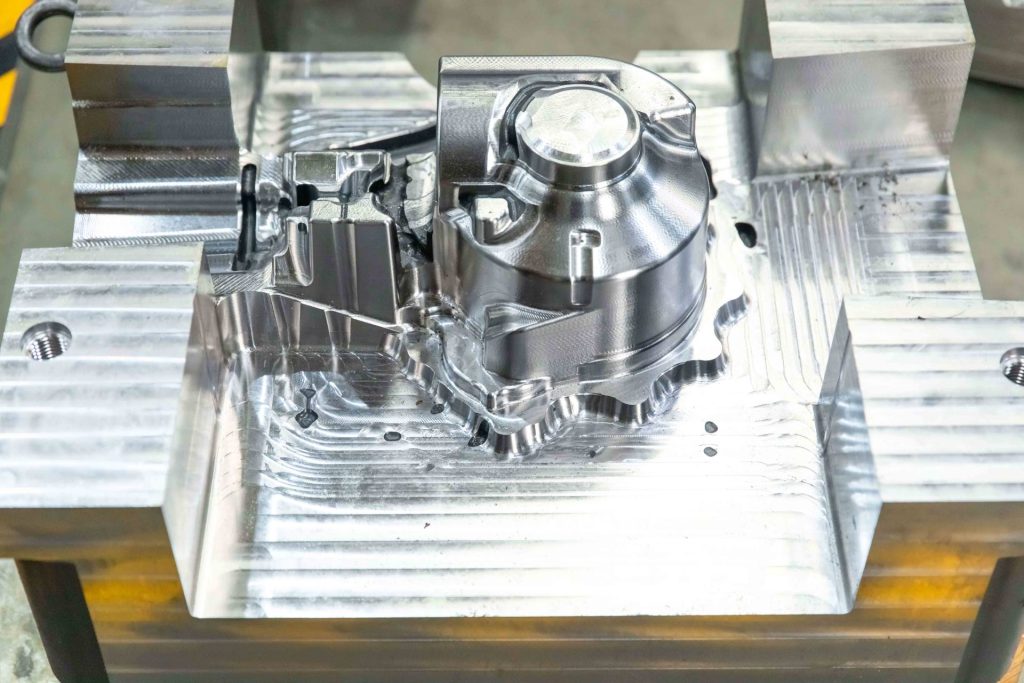
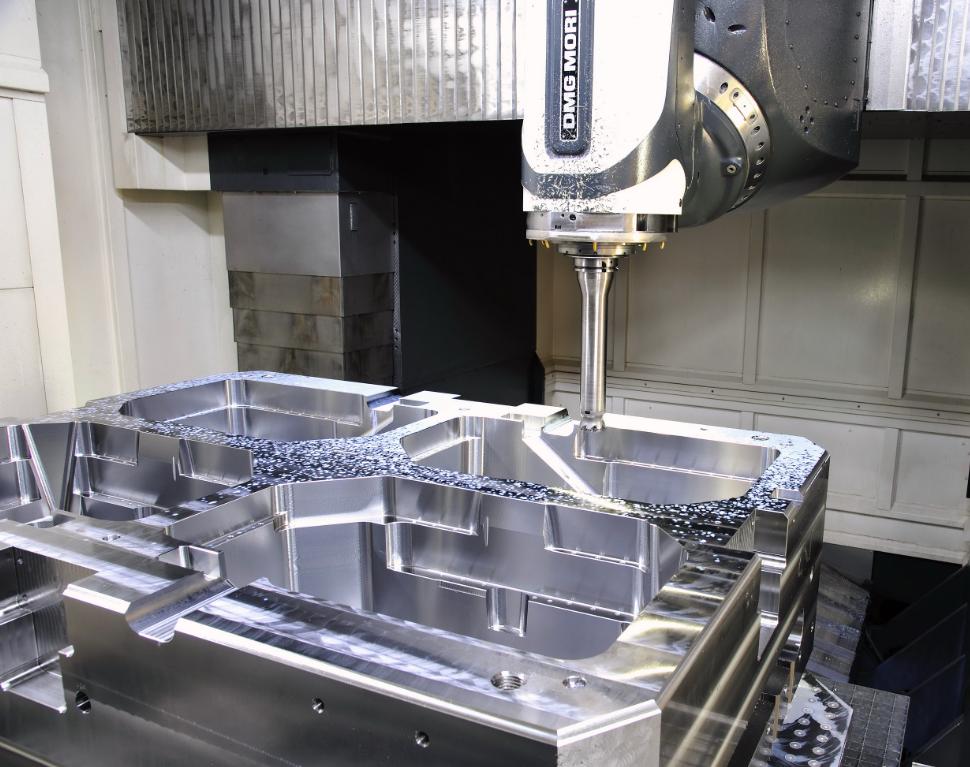
With the manufacturing industry’s escalating demand for rapid iteration and cost control, CNC aluminum molds are reshaping the mold industry landscape through their unique performance advantages. Compared to traditional steel molds, aluminum molds boast a density of only 2.7 g/cm³ (one-third that of steel) and a thermal conductivity of 237 W/m·K (three times higher than steel), enabling significantly faster cooling and machining cycles. According to Grand View Research, the global aluminum mold market reached $1.2 billion in 2023, with the consumer electronics sector accounting for over 40% of this share. The rise of aluminum molds has not only addressed pain points in small-batch, multi-variety production but has also accelerated innovation in industries such as 3C electronics and new energy vehicles.

Materials for CNC Aluminum Mold Manufacturing
If molds are the “mother machines” of industrial production, then materials constitute their genetic code – where subtle alloy adjustments can trigger exponential performance leaps.
Common Aluminum Mold Alloys
Aluminum alloys are the foundation of CNC mold making, with specific grades selected for their unique properties:
- 7075 Aluminum: Known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, 7075 is often chosen for molds requiring exceptional durability. Deployed in Boeing 787 door hinge molds, this alloy withstands 200MPa cyclic loading for 120,000 cycles, outperforming 6061 by 80%. However, it’s worth noting that 7075 can be more challenging to machine compared to other alloys.
- 6061 Aluminum: This alloy is widely favored for its excellent machinability, weldability, and corrosion resistance. It offers a good balance of strength and formability, making it a versatile choice for various molding applications. It’s generally considered easier to machine than 7075.
- 5083 Aluminum: Renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments, 5083 is often used for molds exposed to harsh conditions.
Each alloy’s properties, like thermal conductivity and hardness, influence the mold’s performance. For example, higher thermal conductivity enables faster cooling cycles in injection molding. The selection process therefore require careful considerations of the intended applications.
Material Selection Criteria
Choosing the appropriate aluminum alloy involves evaluating several crucial factors:
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat transfer, reducing cycle times in processes like injection molding.
- Machinability: The ease with which an alloy can be machined impacts production time and cost. 6061 is often preferred for its superior machinability.
- Strength and Hardness: These properties determine the mold’s durability and resistance to wear and deformation. 7075, for example, is chosen for high strength.
- Cost Considerations: Different alloys have varying costs, and the selection must align with the project’s budget.
- Intended Application of the Mold: The specific molding process, the material being molded, and the required production volume all play a role in alloy selection.
The selection of appropriate materials is a balance of intended function, and manufacturing efficiency. Material selection builds the genetic library, but transforming these alloys into precision tools demands breakthrough manufacturing technologies.
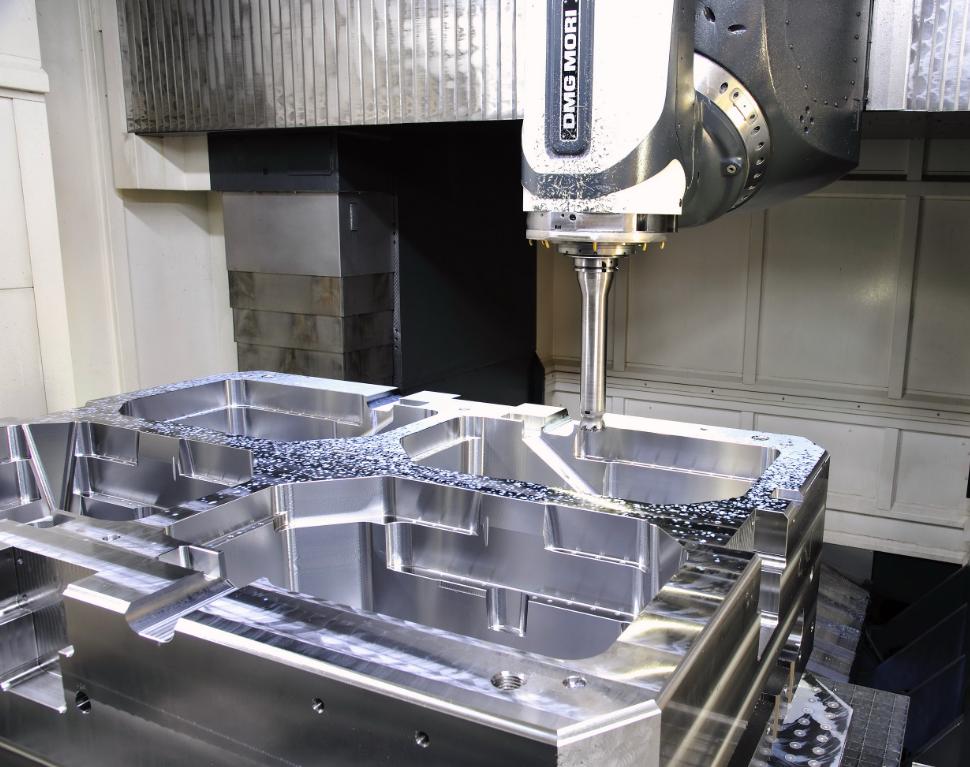

Core Technologies in CNC Mold Making
The success of CNC aluminum mold making relies heavily on the technologies and processes that drive precision, efficiency, and quality. Core technologies in this field integrate advanced design tools, machining strategies, and surface treatments to create molds that meet exacting industrial standards. Here are the CNC mold-making process and the key technologies.
Process Flow
- 3D Modeling: The process begins with creating a detailed 3D model of the mold using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This step ensures that the design specifications, including dimensions and intricate features, are accurately represented for machining.
- Toolpath Planning: Using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software, engineers define the tool paths, cutting strategies, and machining parameters. This step optimizes the machining process for precision, efficiency, and material conservation.
- Rough Machining: Rough machining is performed to remove the bulk of the material quickly. Typically, the spindle runs at 12,000 RPM with a cutting depth of 5 mm, prioritizing speed and efficiency while leaving extra material for subsequent stages.
- Semi-Finishing: Semi-finishing focuses on achieving near-final dimensions with improved accuracy. With tolerances set to ±0.05 mm, this step bridges the gap between rough and fine machining, ensuring a balance between speed and precision.
- Finishing: The finishing stage ensures the final product meets the highest standards of precision and surface quality. Achieving a surface roughness of Ra ≤ 0.4 μm, this step involves meticulous machining to create a flawless mold surface ready for use or further treatment.
- Surface Treatment: After machining, the mold undergoes surface treatments such as polishing, anodizing, or coating. These processes enhance the mold’s durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance, ensuring it meets application-specific requirements.
Precision Control
CNC technology excels in achieving high levels of precision, with tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches. This accuracy is critical for:
- Creating intricate designs and features.
- Ensuring repeatability in high-volume production.
- Reducing material waste and machining errors.
Advanced sensors and real-time monitoring systems further enhance precision, ensuring the mold’s quality and performance.
Surface Treatments
Surface treatments improve the functionality and lifespan of aluminum molds, some common treatments are:
- Polishing: Creates a smooth, mirror-like surface that improves product aesthetics and eases part release during molding.
- Anodizing: Forms a protective oxide layer, increasing corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
- Specialized Coatings: Options like PTFE or ceramic coatings enhance wear resistance and thermal properties, extending the mold’s service life.
The role of surface treatments goes beyond aesthetics. They contribute to reduced wear and tear, enhanced thermal performance, and better compatibility with specific molding applications. These enhancements ensure that molds maintain their quality over extended periods, even under rigorous usage.
As materials and technologies achieve deep integration, aluminum molds are expanding their industrial frontiers.
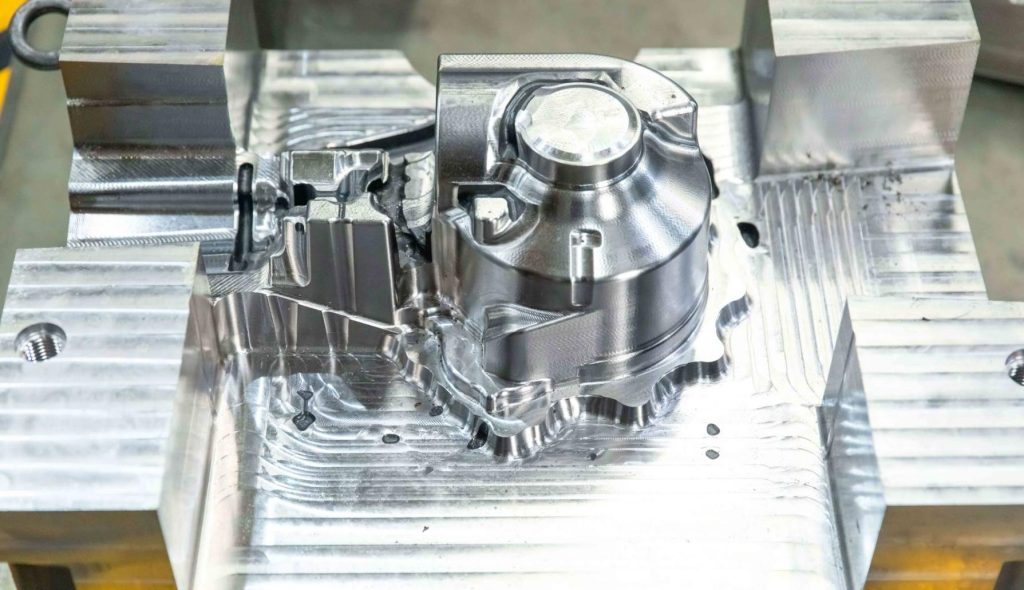

Applications of CNC Aluminum Molds
CNC aluminum molds are utilized in a wide array of industries:
Consumer Electronics
In the consumer electronics industry, CNC aluminum molds are essential for manufacturing enclosures, connectors, and intricate components:
- Smartphone Housings: Aluminum molds enable the production of lightweight and durable cases.
- Connector Housings: Precision molds ensure high compatibility and performance for electronic connectors.
The fast prototyping capabilities of CNC aluminum molds help electronics manufacturers accelerate product development cycles.
Automotive
The automotive sector benefits significantly from CNC aluminum molds in applications such as:
- Prototype Components: Rapid production of prototypes for testing and validation.
- Lightweight Parts: Molds for aluminum-based components like brackets and housings contribute to vehicle weight reduction.
- Custom Tooling: Specialized molds for one-off or custom parts used in motorsport and performance vehicles.
By leveraging CNC aluminum molds, automakers achieve cost savings and design flexibility without compromising performance.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, CNC aluminum molds are critical for producing precise and sterile components:
- Surgical Instruments: High-precision molds ensure the accuracy and reliability of surgical tools.
- Diagnostic Equipment: Molds for casings and intricate parts used in medical devices.
- Prosthetics: Custom molds enable the production of personalized prosthetics with excellent fit and finish.
The use of aluminum molds ensures that medical components meet stringent regulatory and quality standards, contributing to improved patient outcomes.
CNC aluminum mold making represents a transformative approach to modern manufacturing. The properties of aluminum, coupled with the precision of CNC machining, enable the creation of molds for a diverse range of applications, from consumer electronics to automotive and medical devices. As CNC technology advances and new aluminum alloys are developed, the capabilities and applications of aluminum mold making will continue to expand.