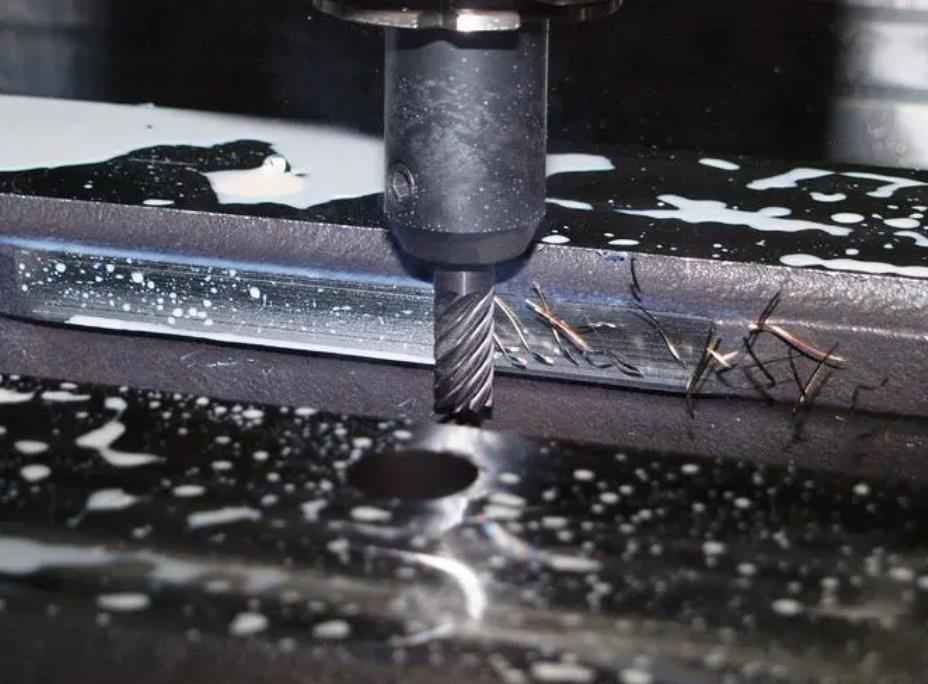
CNC milling is a popular machining process used to create precise and complex parts for a wide range of industries. To achieve the best results, it’s important to optimize the speed and feed rate of the milling process based on the material being milled. Aluminum is a common material used in CNC milling due to its lightweight, high strength, and excellent machinability. However, achieving the right speed and feed rate for milling aluminum can be a challenge, as it requires balancing between efficient material removal and maintaining a high-quality surface finish. In this article, we’ll explore the factors that impact the CNC milling speed and feed rate for aluminum, and provide some tips for optimizing the milling process for this material.

What are the impacting factors of aluminum CNC milling feeds and speeds?
Several factors can impact the CNC milling speed and feed rate for aluminum. Here are some of the key factors to consider:
Aluminum Alloy: Different aluminum alloys have varying properties that affect the milling process. For example, 6061-T6 aluminum has a higher tensile strength than 2024-T3 aluminum, which affects the recommended cutting speed and feed rate.
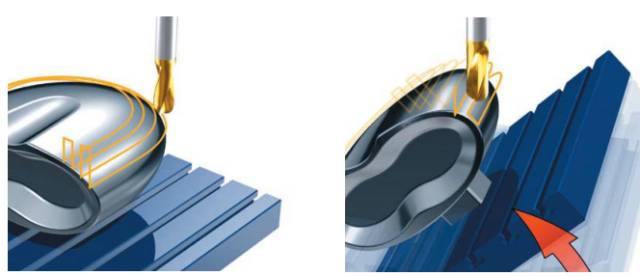
Cutting Tool Geometry: The geometry of the cutting tool, such as the number of flutes and the helix angle, can affect the chip formation and the heat generated during the milling process. This, in turn, affects the recommended speed and feed rate for milling aluminum.
Cutting Tool Coating: Coatings on the cutting tool can improve tool life and reduce friction, allowing for higher speeds and feeds. However, different coatings are recommended for different materials, so it’s important to select the right coating for aluminum milling.
Depth of Cut: The depth of cut is the amount of material removed in a single pass of the cutting tool. A deeper cut can increase material removal rates, but it also increases the risk of tool deflection and poor surface finish.
Coolant/Lubrication: Using coolant or lubrication can reduce the heat generated during the milling process, which can help prevent tool wear and improve surface finish. However, the type of coolant/lubrication and its application method can impact the recommended speed and feed rate.
Machine Rigidity: The rigidity of the milling machine can impact the recommended speed and feed rate, as a more rigid machine can handle higher speeds and feeds without sacrificing accuracy.
By taking these factors into account and adjusting the milling speed and feed rate accordingly, it’s possible to optimize the milling process for aluminum and achieve high-quality, accurate parts. So do you know how to optimize the CNC milling speed and feed rate for aluminum? Here are some tips:
How to optimize the aluminum CNC milling feeds and speeds?
Determine the appropriate cutting speed: CNC milling aluminum speed can typically range from 400 to 1200 SFM (Surface Feet per Minute), depending on the type of aluminum alloy and the tool being used. The cutting speed should be set within this range to ensure efficient material removal while avoiding excessive tool wear.
Select the right tool: For aluminum milling, it is recommended to use high-speed steel or carbide tools, as they are designed to withstand high cutting speeds and reduce tool wear.
Choose the right feed rate: The feed rate is the distance the tool travels in one revolution of the spindle. Typically, the feed rate for aluminum milling ranges from 0.001 to 0.02 inches per tooth, depending on the cutter diameter, tool geometry, and cutting conditions.
Optimize the depth of cut: The depth of cut is the amount of material removed in one pass. For aluminum, the recommended depth of cut is usually between 0.05 and 0.25 inches, depending on the machine’s rigidity, the cutting tool, and the specific application.
Use coolant: Cooling is essential when milling aluminum to prevent chip buildup and to keep the tool cool, prolonging its life. Use a water-soluble cutting fluid, which is designed for use on non-ferrous materials.
Experiment and adjust the parameters: Once the initial settings are chosen, adjust the parameters based on the machine’s performance and the specific aluminum material being used. Be sure to monitor the tool wear and surface finish quality to ensure that the parameters are producing the desired results.
By following these general guidelines and optimizing the cutting parameters based on the specific application and material being used, it is possible to achieve the optimal speed and feed rate for aluminum milling.
As the type of tool is an important factor that influences the milling speed and feed. Therefore, in general, the following types of cutting tools are commonly used for milling aluminum:
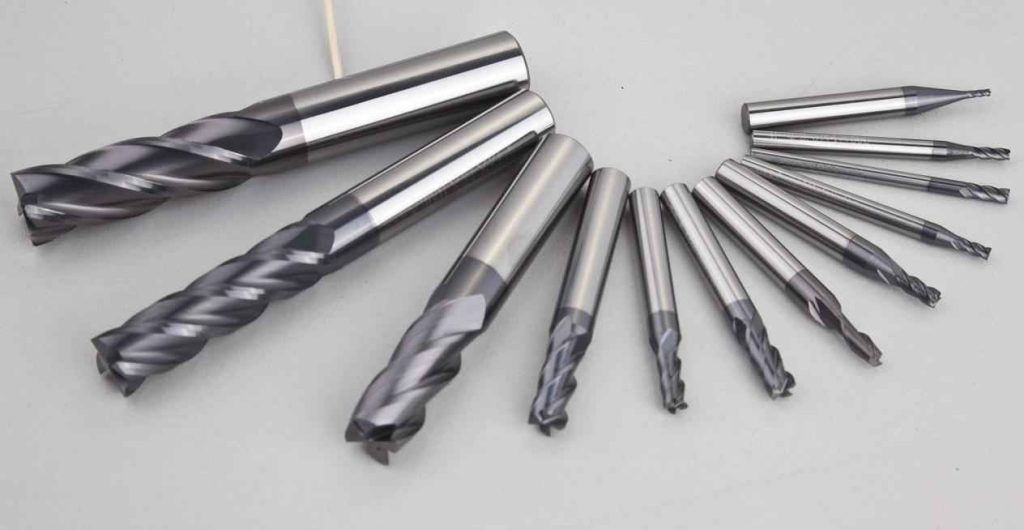

What is the best CNC milling cutter for milling aluminum?
Carbide end mills – Carbide is a hard and wear-resistant material that can withstand the high cutting temperatures generated during milling. Carbide end mills are ideal for milling aluminum due to their ability to remove material quickly and efficiently.
High-speed steel (HSS) end mills – HSS end mills are a popular choice for milling aluminum because they are less expensive than carbide end mills and can still provide good performance. HSS end mills are also more flexible and less brittle than carbide, making them less prone to breakage.
Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) end mills – PCD end mills are another option for milling aluminum. They are made of a diamond material that is chemically bonded to a carbide substrate. PCD end mills offer excellent wear resistance and can maintain their sharpness for longer periods than carbide or HSS end mills.
All in all, the best cutting tool for CNC milling aluminum will depend on the specific requirements of the application. It’s essential to select the right tool for the job, taking into account factors such as cutting speed, feed rate, and material hardness to achieve the desired results. Or if you need to find a professional CNC milling manufacturer, JTR is a pleasure to serve you. JTR provides you with a reliable one-stop CNC machining service, which provides rapid prototyping/end-use part production in a variety of materials, and related machining services to small, medium, and large-sized parts. Please feel free to contact us.