Molds are produced by injection molding, blow molding, extrusion, die casting or forging, smelting, stamping, and other methods. Simply put, molds are used to make shaped objects. The tool consists of several components. Different molds are made from different parts. So do you know how the mold is made? What are the manufacturing technologies of molds? This article sorts out the 5 most common processing methods for mold making, you must spend five minutes to read the full text.
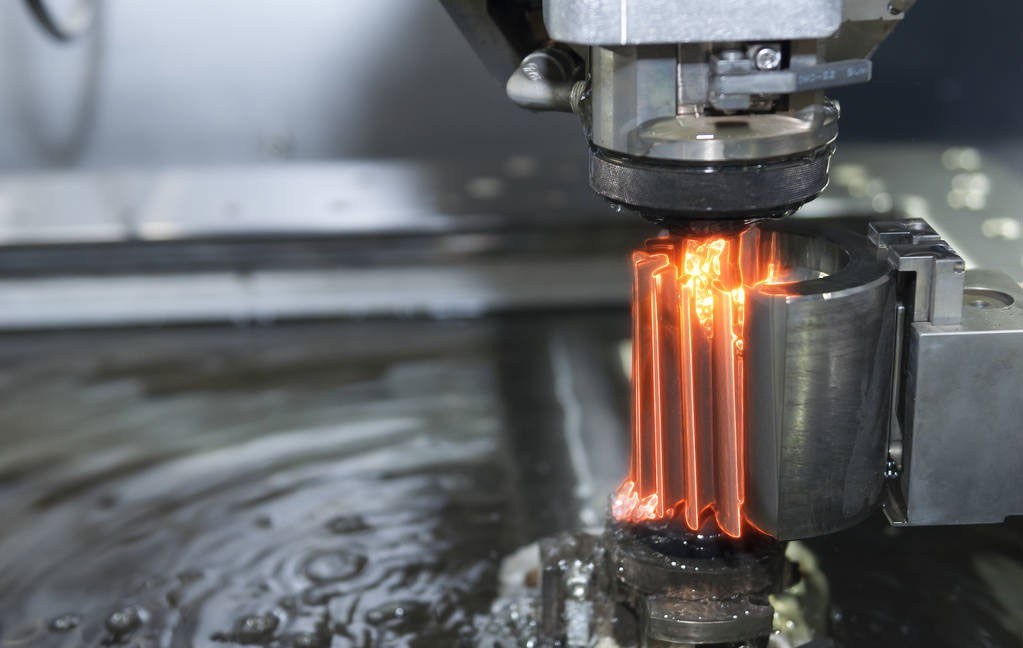

1. EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining)
How does EMD work?
EDM is a special machining method that uses the electro-erosion effect generated by the pulse discharge between the two poles immersed in the working fluid to erode conductive materials, also known as electric discharge machining or electro-erosion machining.

EDM is suitable for the processing of complex parts such as precision small cavities, narrow slits, grooves, and corners. When it is difficult for the tool to reach complex surfaces, where deep cuts are required, and where the aspect ratio is particularly high, the EDM process is preferred over milling.
For the machining of high-tech parts, re-discharge of the milling electrode can improve the success rate, and EDM is more suitable than the high and expensive tool cost. In addition, where EDM finishing is specified, EDM is used to provide a fire pattern surface. With the rapid development of high-speed milling today, the development space of EDM has been squeezed to a certain extent.
At the same time, high-speed milling has also brought greater technological progress to EDM. For example, using high-speed milling to manufacture electrodes, the number of electrode designs is greatly reduced due to the realization of small area machining and high-quality surface results. In addition, using high-speed milling to manufacture electrodes can also improve the production efficiency to a new level, and can ensure the high precision of the electrodes, so that the accuracy of EDM is also improved.
Advantages of EDM:
- EDM can process materials and complex-shaped workpieces that are difficult to cut by ordinary cutting methods; no cutting force during processing; no defects such as burrs and tool marks and grooves.
- The tool electrode material does not need to be harder than the workpiece material; it is easy to realize automation by directly using electrical energy to process.
- EDM can process any conductive materials with high strength, high hardness, high toughness, high brittleness, and high purity; there is no obvious mechanical force during processing, and it is suitable for processing low-rigidity workpieces and microstructures.
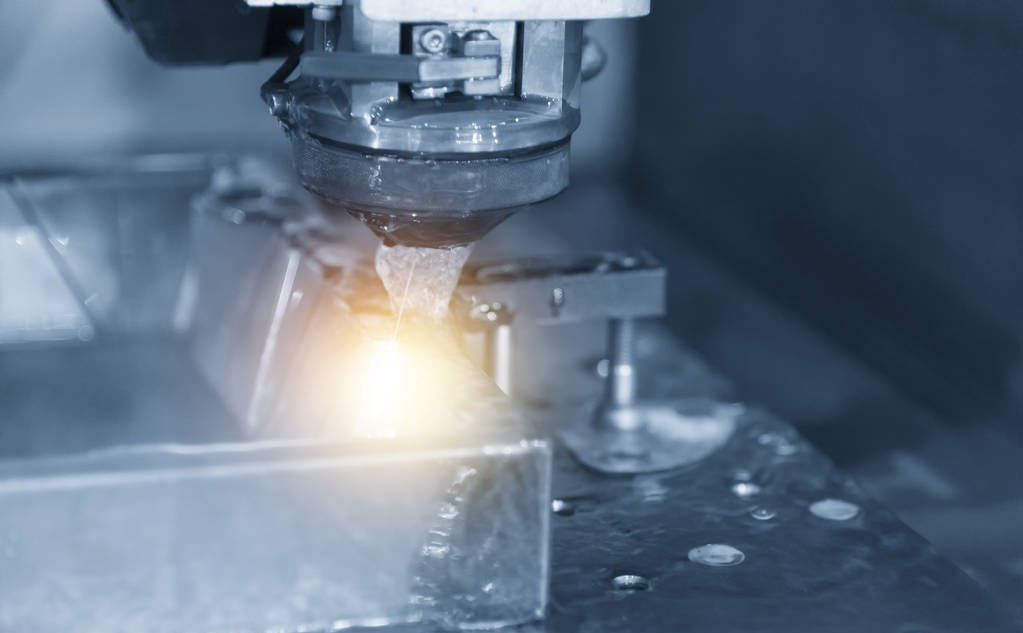
2. WEDM (Wire Cut Electrical Discharge Machining)
How does wire WEDM work?
Using a continuously moving thin wire (called an electrode wire) as an electrode, a pulsed spark discharge is performed on the workpiece to remove metal and cut to shape.

Advantages of WEDM:
In addition to the basic features of EDM, WEDM has some other features:
① No need to manufacture tool electrodes with complex shapes, any two-dimensional curved surface with a straight line as a generatrix can be processed;
②It can cut narrow slits of about 0.05 mm;
③ During processing, all excess materials are not processed into waste chips, which improves the utilization rate of energy and materials;
④In the low-speed wire EDM process where the electrode wire is not recycled because the electrode wire is constantly updated, it is beneficial to improve the machining accuracy and reduce the surface roughness;
⑤ The cutting efficiency that WEDM can achieve is generally 20-60 mm2/min, up to 300 mm2/min; the machining accuracy is generally ±0.01 to ±0.02 mm, up to ±0.004 mm; surface roughness Generally Ra2.5 to 1.25 microns, up to Ra0.63 microns; cutting thickness is generally 40-60 mm, the maximum thickness can reach 600 mm.
3. Electro-Chemical Machining
How does Electro-Chemical Machining work?
Electro-Chemical Machining is a process method based on the principle of anode dissolution in the electrolysis process and with the help of the formed cathode, the workpiece is processed into a certain shape and size.
Electrochemical machining has significant advantages for machining difficult-to-machine materials, complex-shaped or thin-walled parts. Electrochemical machining has been widely used, such as barrel rifling, blades, integral impellers, molds, special-shaped holes, and parts, chamfering and deburring. And in the processing of many parts, the electrolytic machining process has occupied an important and even irreplaceable position.
Advantages of Electro-Chemical Machining
A wide range of processing. Electrochemical machining can process almost all conductive materials and is not limited by the strength, hardness, toughness, and other mechanical and physical properties of the material, and the metallographic structure of the material does not change after processing. It is often used for machining hard-to-machine materials such as cemented carbide, superalloy, hardened steel, and stainless steel.
Limitations of Electro-Chemical Machining
The machining accuracy and machining stability are not high; the machining cost is high, and the smaller the batch, the higher the additional cost per piece.
4. Ion Beam Machining
How does Ion Beam Machining work?
Ion beam machining is to realize the machining of parts by accelerating and focusing the ion current generated by the ion source on the surface of the workpiece in a vacuum state.
Advantages of Ion Beam Machining
Since the ion current density and ion energy can be precisely controlled, the processing effect can be precisely controlled, and ultra-precision processing at the nano-level or even the molecular and atomic level can be realized.
During ion beam Machining, the pollution generated is small, the processing stress and deformation are extremely small, and the adaptability to the material to be processed is strong, but the processing cost is high.

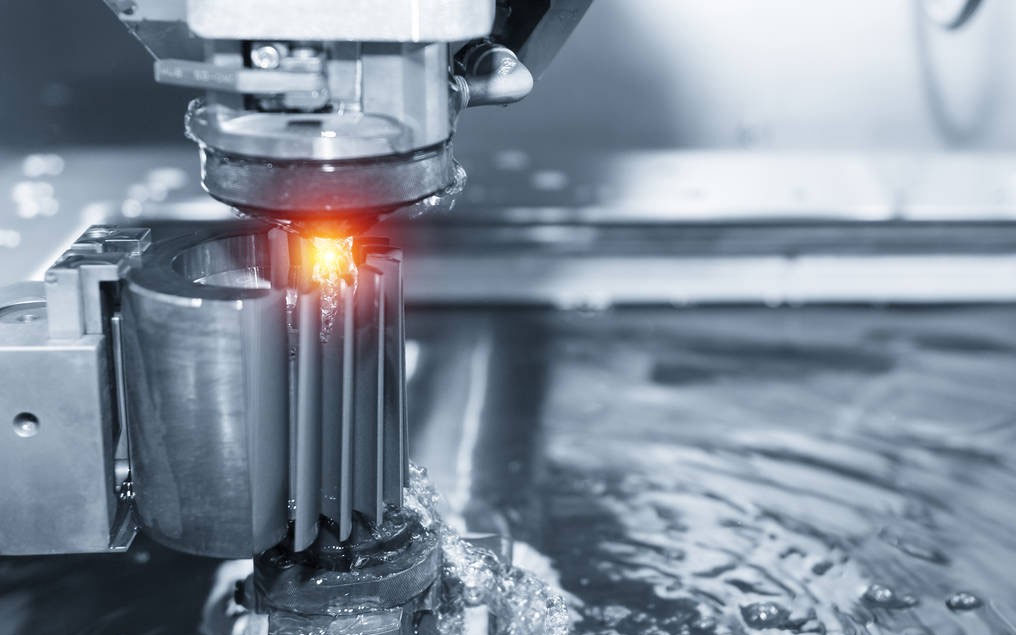
5. Chemical Etching
How does Chemical Etching work?
Chemical Etching is a special process that uses acid, alkali, or salt solution to corrode and dissolve the workpiece material to obtain the desired shape, size, or surface state of the workpiece.
Advantages of Chemical Etching
1) Can process any metal material that can be cut, not limited by hardness, strength, and other properties;
2) Suitable for large-area processing, and can process multiple pieces at the same time;
3) No stress, crack, burr, the surface roughness of Ra1.25-2.5μm;
4) Easy to operate;
5) It is not suitable for processing narrow slots and holes;
6) It is not advisable to eliminate defects such as uneven surfaces and scratches.
The scope of use of chemical etching
Suitable for large area thickness reduction processing; suitable for processing complex holes on thin-walled parts.