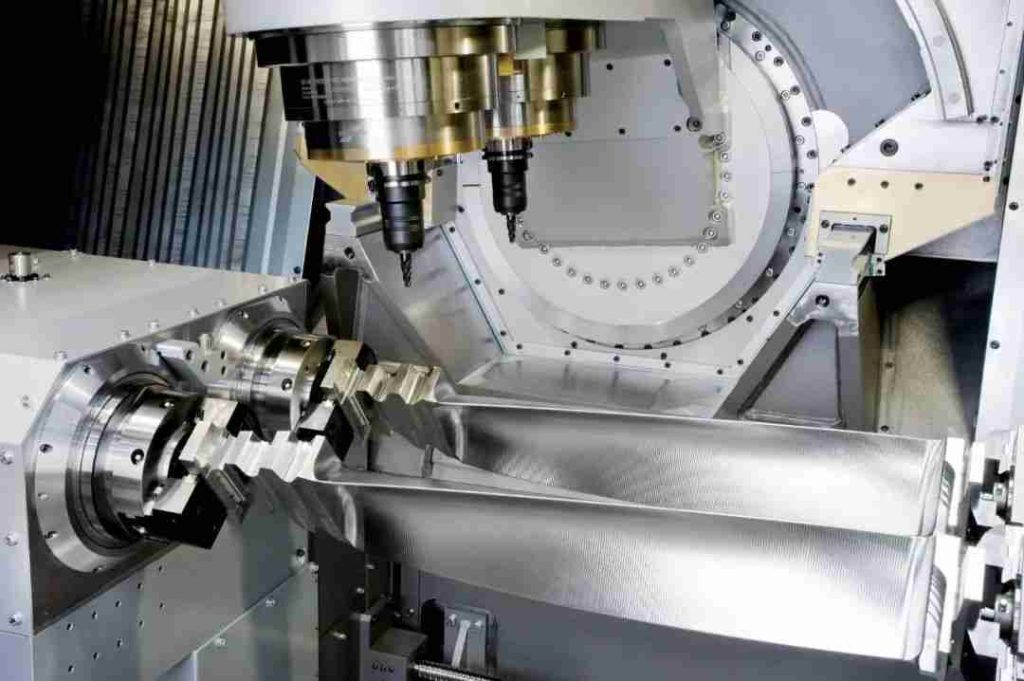
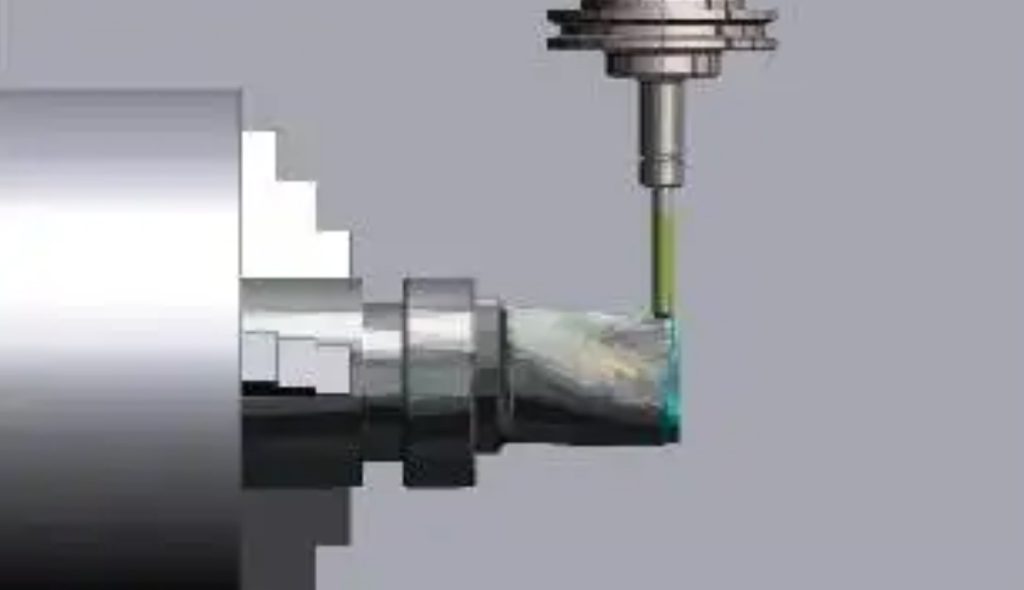
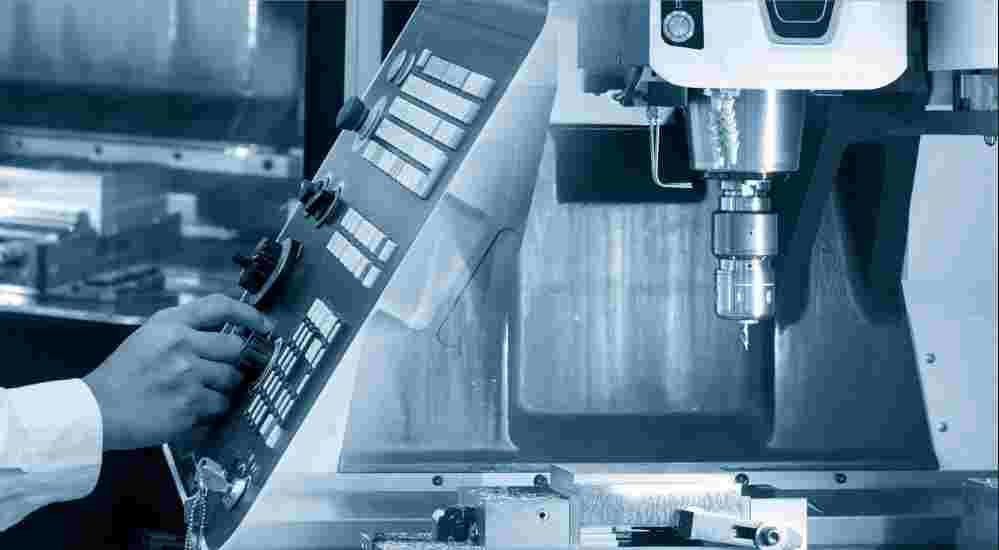
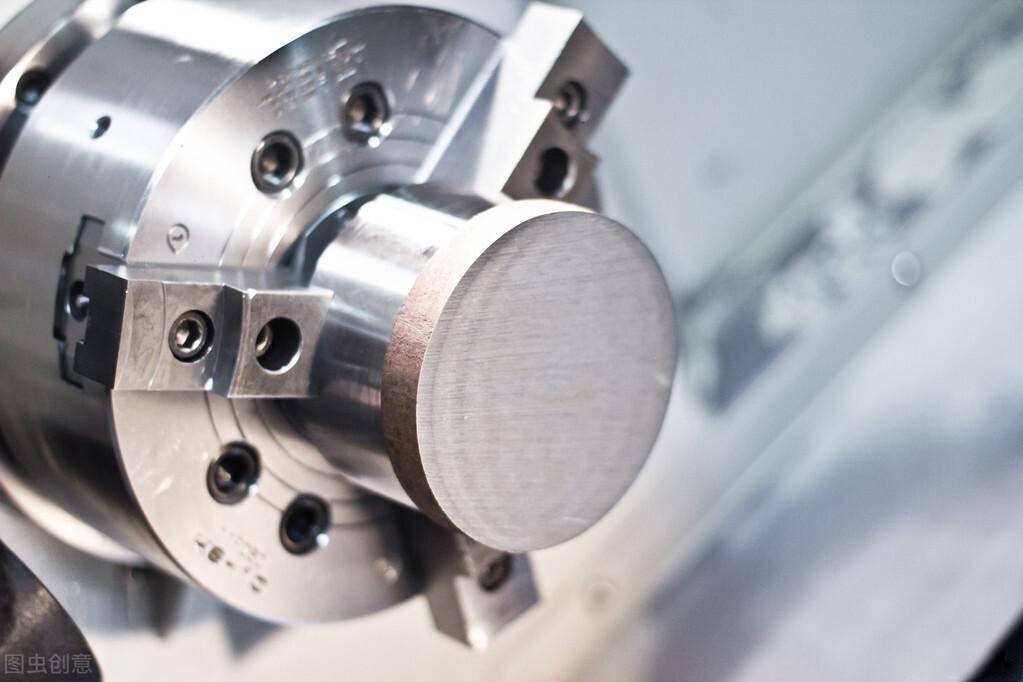
CNC drilling is a type of machining process that uses a computer-controlled machine to drill holes in materials. In CNC drilling, a computer program is used to control the drilling machine’s movements and actions, including the position and speed of the drill bit, the depth of the hole, and the rate of material removal. In this article, we’ll explore four essential pieces of knowledge about CNC drilling, including the tools and equipment used, and the steps and precautions involved in the process. Hope this article can help you to choose the proper CNC machining process.

1. Overview of the steps in CNC drilling
CNC drilling is a multi-step process that involves several different stages. Here is an overview of the typical steps involved in CNC drilling:
- Design: The first step in CNC drilling is to create a digital model of the part or component to be drilled using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The model includes information about the shape, size, and location of the holes to be drilled.
- Programming: Once the design is complete, the drilling machine is programmed using computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. The program specifies the location, size, and depth of each hole and sets the drilling parameters, such as speed and feed rate.
- Setup: The material to be drilled is mounted on the drilling machine’s worktable and secured in place using clamps or other fixtures. The drilling machine is then set up according to the program’s specifications, including the position and speed of the drill bit.
- Drilling: Once the drilling machine is set up, the drilling process begins. The drill bit is lowered onto the material and rotated at high speed to remove the material and create the desired hole shape and size. The drilling machine is controlled by the program, which ensures that the hole is drilled to the exact specifications of the model.
- Inspection: Once the drilling process is complete, the part or component is inspected to ensure that the holes have been drilled to the correct size, depth, and location. Any defects or errors are identified and corrected as necessary.
- Finishing: Depending on the application, the drilled part or component may undergo additional finishing processes, such as deburring or polishing, to remove any rough edges or surface imperfections.
Overall, CNC drilling is a highly precise and efficient process that allows manufacturers to create complex parts and components with ease. By automating the drilling process and using computer-controlled machines, manufacturers can produce parts with a high degree of accuracy and consistency, while also reducing costs and lead times.
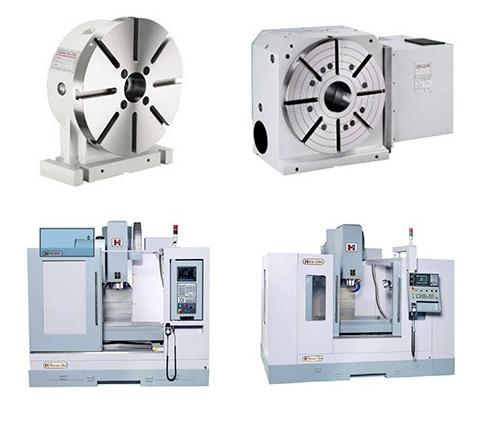

2. What are CNC drilling equipment and tools?
CNC drilling requires a range of specialized tools and equipment to perform the drilling process accurately and efficiently. Here are some of the key tools and equipment used in CNC drilling:
CNC Drilling Machine: A CNC drilling machine is a computer-controlled machine that can accurately and precisely drill holes in a wide range of materials. The machine is equipped with a spindle that rotates the drill bit at high speeds and can move in multiple axes to create holes of various shapes and sizes.
Drill Bit: The drill bit is the cutting tool that removes material and creates a hole in the material being drilled. Drill bits come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and the type of bit used will depend on the material being drilled and the size and shape of the hole required.
Chuck: The chuck is the device that holds the drill bit in place on the spindle. It allows the drill bit to be easily swapped out for different sizes and shapes.
Worktable: The worktable is the surface on which the material to be drilled is mounted. It is typically made of metal and is adjustable in height and angle to accommodate different sizes and shapes of materials.
Clamps and Fixtures: Clamps and fixtures are used to secure the material being drilled to the work table, ensuring that it remains in place during the drilling process. These can include vice grips, C-clamps, and specialized fixtures designed for specific materials.
CAD/CAM Software: CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is used to create a digital model of the part or component to be drilled, while CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software is used to program the CNC drilling machine to drill the holes to the exact specifications of the model.
Measuring Tools: Measuring tools such as micrometers, calipers, and gauges are used to ensure that the drilled holes meet the required specifications in terms of size, depth, and location.
Overall, CNC drilling requires a range of specialized tools and equipment to ensure that the drilling process is accurate, efficient, and precise. By using high-quality equipment and tools and ensuring that they are properly maintained, manufacturers can achieve high-quality results and produce complex parts and components with ease.

3. Detailed precautions in the process
- Material Selection
The first step in the CNC drilling process is to select the appropriate material to be drilled. The material must be able to withstand the drilling process without warping or breaking and should also be compatible with the type of drill bit being used. Common materials used in CNC drilling include metals, plastics, composites, and ceramics.
- Toolpath Planning
Once the material has been selected, the next step is to create a digital model of the part or component to be drilled using CAD software. The model includes information about the location, size, and shape of the holes to be drilled. The CAM software is then used to generate a toolpath, which is a sequence of movements that the drill bit will follow to create the holes. The toolpath takes into account the material properties, drill bit size, and other factors to ensure that the drilling operation is efficient and precise.
- Setup
Once the toolpath has been generated, the material is mounted on the CNC drilling machine’s worktable and secured in place using clamps or other fixtures. The drill bit is then selected based on the material being drilled and the size and shape of the holes required. The drill bit is installed in the spindle of the drilling machine, and the drilling parameters, such as the speed and feed rate, are set according to the toolpath.
- Drilling Operation
With the setup complete, the drilling operation begins. The drill bit is lowered onto the material, and the spindle is rotated at high speeds to remove the material and create the desired hole shape and size. The CNC drilling machine follows the toolpath created in the CAM software, ensuring that the hole is drilled to the exact specifications of the model.
- Inspection
Once the drilling operation is complete, the part or component is inspected to ensure that the holes have been drilled to the correct size, depth, and location. Any defects or errors are identified and corrected as necessary.
- Finishing
Depending on the application, the drilled part or component may undergo additional finishing processes, such as deburring or polishing, to remove any rough edges or surface imperfections. This helps to improve the overall quality and appearance of the final product.
Overall, CNC drilling is a highly precise and efficient process that allows manufacturers to create complex parts and components with ease. By automating the drilling process and using computer-controlled machines, manufacturers can produce parts with a high degree of accuracy and consistency, while also reducing costs and lead times.