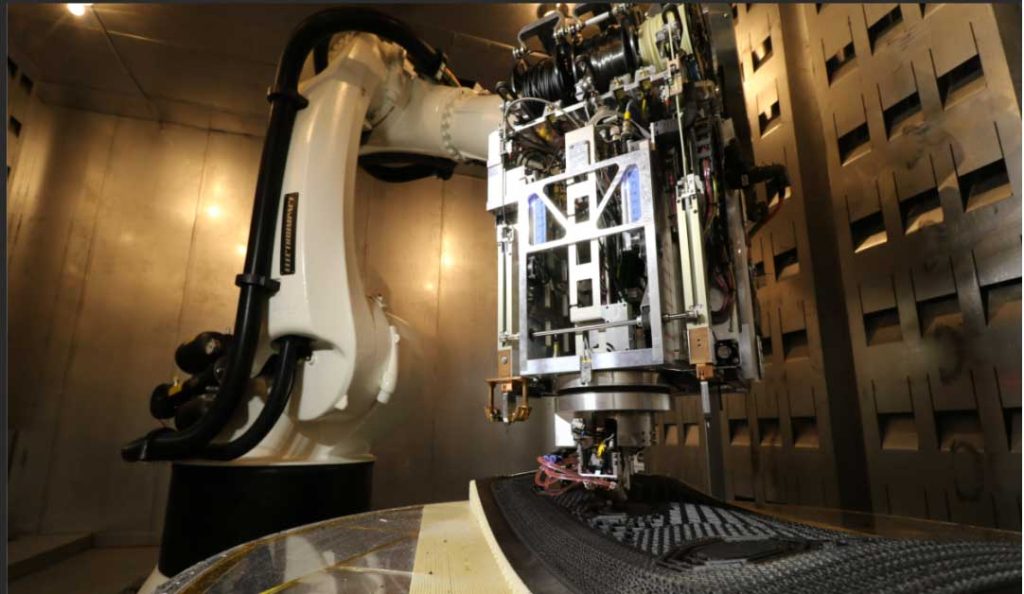
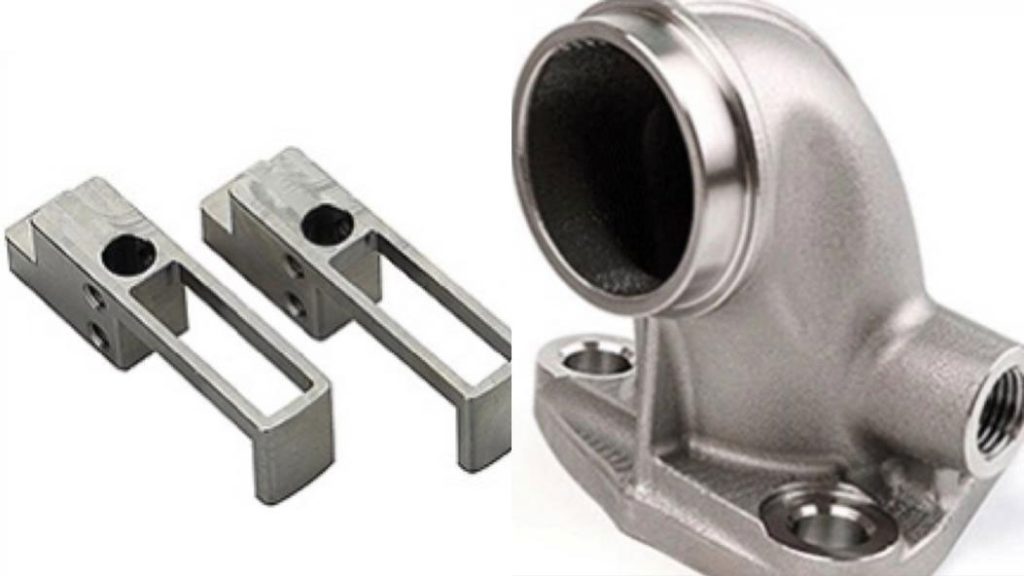
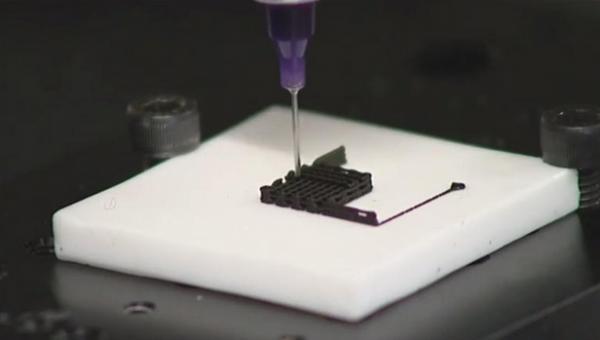
Over the last few decades, 3D printing has revolutionized the manufacturing industry by enabling faster, more efficient, and more cost-effective production of a wide range of products. From customized medical implants to intricate jewelry designs, 3D printing has opened up new possibilities for manufacturers in a variety of industries. As technology continues to advance, new applications for 3D printing are emerging all the time. In this article, we will explore 10 of the latest 3D printing applications, including those in fields such as aerospace, fashion, and food production. With the potential for increased customization, reduced waste, and improved efficiency, it’s clear that 3D printing is set to play an even greater role in the manufacturing industry in the years to come.

10 Latest 3D Printing Applications
3D Printing in Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace and defense industries have been early adopters of 3D printing technology, which has opened up new possibilities for the design and production of complex and high-performance parts.
For example, 3d printing in aerospace enables the production of lightweight structures with complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods. The engine components such as turbine blades and fuel nozzles, which require high precision and durability are also made by 3D printing.
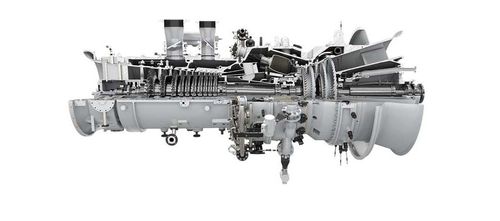
3D Printing Medical Devices
3d printing technology had a significant impact on the medical device industry. One of the biggest impacts is 3d printing medical devices can be customized to the demand of patients.
For example, 3D printing is used to produce customized prosthetics for patients, allowing for a precise fit and greater functionality. Also, 3D printing enables the production of implants with complex geometries, such as hip and knee replacements that better match the patient’s anatomy, leading to improved outcomes and reduced risk of implant failure. Some surgical instruments such as forceps and clamps, can be customized to the needs of individual surgeons and procedures.
3D Printing in Architecture
3D printing is increasingly being used in architecture to produce detailed and intricate models of buildings, as well as to create custom components and prototypes, allowing architects to better visualize and communicate their designs to clients and stakeholders.
Moreover, 3D printing is used to produce building components using sustainable and eco-friendly materials such as bioplastics and recycled materials. This enables architects to design more sustainable and environmentally friendly buildings, while also reducing waste and material costs.
3D Printing in Jewelry
3D printing has revolutionized the jewelry industry by enabling the production of intricate and unique designs with greater precision and speed.
For example, 3D printing is used to produce custom jewelry designs, allowing for greater design flexibility and customization. There is a wide range of materials used in 3D printing, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. And it can produce jewelry in small batches or on demand, reducing the need for large production runs and the associated inventory costs.
3D Printing in Education
3D printing has become an increasingly popular tool in education, as it enables students to learn and explore complex concepts and ideas in a hands-on and interactive way.
For example, 3D printing is used to teach science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) concepts tangibly and interactively. Students can use 3D printers to design and create physical models of scientific concepts, such as molecules or engineering structures, enabling them to better understand complex ideas. They can also use 3D printers to create physical replicas of historical artifacts, enabling them to better understand the context and significance of these objects.
Moreover, students with visual impairments can use 3D printers to create tactile models of objects and concepts, enabling them to better understand complex ideas.

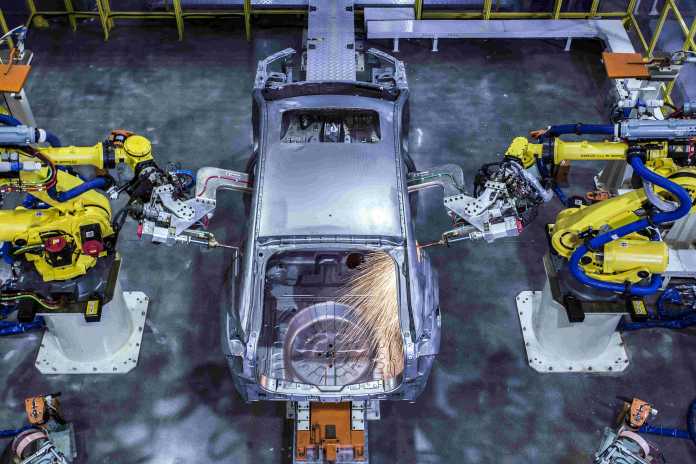
3D Printing in Automotive
In the automotive industry, it is essential to use rapid prototyping techniques before developing the product. The automobile industry extensively uses 3D printing technology. Before developing the final product, they develop 3D-printed parts and test them with the original parts.
3D printing has greatly improved the automotive industry by enabling greater design flexibility and customization, reducing lead times and costs, and enabling the production of complex and lightweight parts with greater efficiency.
3D Printing in Food
3D printing has become an emerging technology in the food industry, with a range of potential applications.
For example, 3D printing is used to create custom-shaped food products that are difficult to make using traditional methods, such as personalized chocolates, candies, or cake toppers. This technology also enables personalized nutrition, where food can be customized to the individual’s specific dietary needs and preferences. In addition, 3D printing is used to preserve perishable food items by creating replicas or molds of food that can be used as a template to recreate the item later. This technique can be especially useful for creating replicas of rare or endangered foods.
3D Printing in Art and Sculpture
3D printing has opened up new possibilities for artists and sculptors, enabling them to create complex and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional techniques.
For example, 3D printing is used to produce prototypes of sculptures and other art pieces, allowing artists to experiment with different designs and make adjustments quickly and easily. Moreover, 3D printing is used to replicate sculptures and other art pieces that may be too delicate or rare to handle, preserving them for future generations.
3D printing also can be used to facilitate collaborative works of art, where multiple artists can contribute to a single piece, even if they are in different locations. With continued advances in 3D printing technology, the possibilities for artistic expression are limitless.

3D Printing in Musical Instruments
3D printing has been used in the production of musical instruments, providing several benefits over traditional manufacturing methods.
For example, 3D printing allows for the customization of musical instruments, such as creating unique designs or tailoring the instrument to a specific musician’s needs. And it allows for the use of a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, and even wood composites, providing new possibilities for instrument construction and sound. With continued advancements in 3D printing technology, the production of musical instruments is likely to become even more accessible and innovative in the future.
3D Printing in Sports Equipment
3D printing has been used in the production of sports equipment, providing new possibilities for customization, lightweight and durable construction, material experimentation, and design innovation.
For example, 3D printing allows for the customization of sports equipment, such as creating unique designs or tailoring the equipment to a specific athlete’s needs. It also allows for the use of a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, and carbon fiber composites, providing new possibilities for equipment construction and performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing is a technology with a vast array of applications across numerous industries. From rapid prototyping and customization in manufacturing to medical implants and even food production, 3D printing continues to push the boundaries of what is possible.